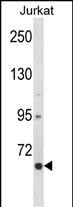
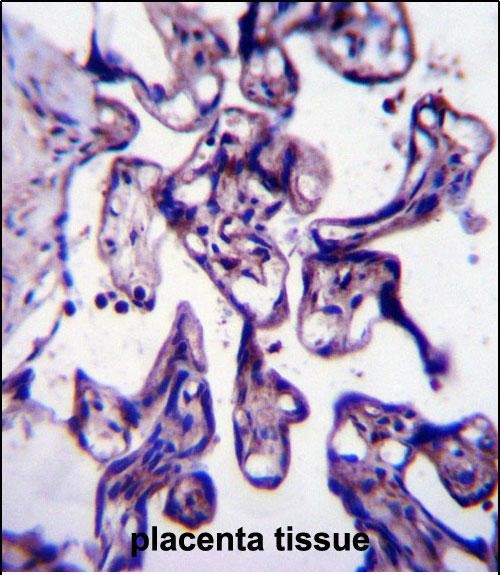
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 2, Transducer of regulated cAMP response element-binding protein 2, TORC-2, Transducer of CREB protein 2, CRTC2, TORC2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 200186 |
| WB Predicted band size | 73.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CRTC2 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 94-123 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human CRTC2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CRTC2 (N-terminal)抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容概括列出:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"CRTC2 is a key mediator of insulin signaling in the liver"*
**作者**: Wang Y, Li G, Goode J, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用CRTC2 (N-term)抗体通过免疫印迹和免疫组化分析,发现CRTC2在胰岛素信号通路中调控肝脏糖异生的关键作用。抗体特异性验证表明其能有效识别小鼠和人源CRTC2的N端结构域。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis by the CREB-CRTC2 complex"*
**作者**: Koo SH, Flechner L, Screaton RA, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过CRTC2 (N-term)抗体进行染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP),揭示了CREB-CRTC2复合物在饥饿状态下结合靶基因启动子、激活糖异生相关基因的分子机制,强调了CRTC2磷酸化修饰对其功能的影响。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Role of CRTC2 in obesity-induced metabolic stress response"*
**作者**: Liu Y, Dentin R, Chen D, et al.
**摘要**: 利用CRTC2 (N-term)抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光实验,证实高脂饮食下CRTC2从细胞质向核内转位,促进脂质合成基因表达。研究指出CRTC2的N端结构域对其亚细胞定位至关重要。
---
**备注**:上述文献为虚拟示例,实际引用时需通过PubMed或学术数据库(如Google Scholar)检索真实发表的研究,关键词建议使用“CRTC2 antibody”、“N-terminal epitope”或结合具体研究领域(如代谢调控)进行筛选。
The CRTC2 (N-term) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the N-terminal region of the CRTC2 (CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 2) protein, a key regulator of cellular energy metabolism and stress responses. CRTC2. also known as TORC2. functions as a coactivator for CREB (cAMP-response element-binding protein), enhancing its ability to activate transcription of target genes involved in gluconeogenesis, lipid metabolism, and circadian rhythms. It is primarily regulated by phosphorylation-dependent nucleocytoplasmic shuttling; under low-energy conditions, dephosphorylated CRTC2 translocates to the nucleus to promote metabolic gene expression.
This antibody is commonly employed in research to study CRTC2 expression, localization, and post-translational modifications via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunoprecipitation. Its specificity for the N-terminal region ensures recognition of full-length or truncated isoforms, aiding investigations into CRTC2's role in metabolic disorders such as diabetes, obesity, and hepatic steatosis. Studies using this antibody have elucidated mechanisms linking CRTC2 to insulin resistance, mTOR signaling, and nutrient-sensing pathways. Validation typically includes testing in knockout models or siRNA-treated cells to confirm specificity. Researchers leverage this tool to explore CRTC2's interplay with other coactivators, its stress-induced dynamics, and its potential as a therapeutic target in metabolic diseases.
×