
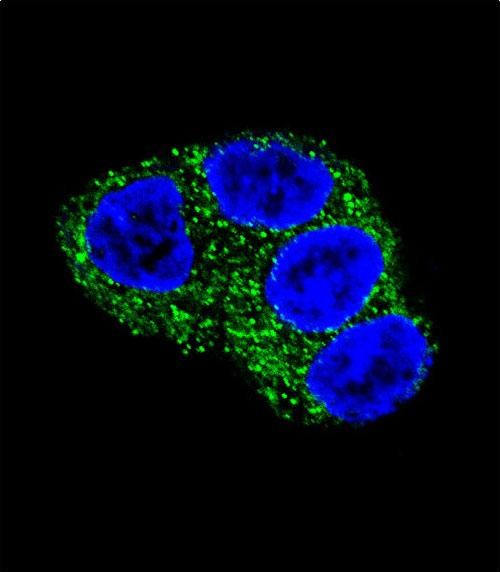
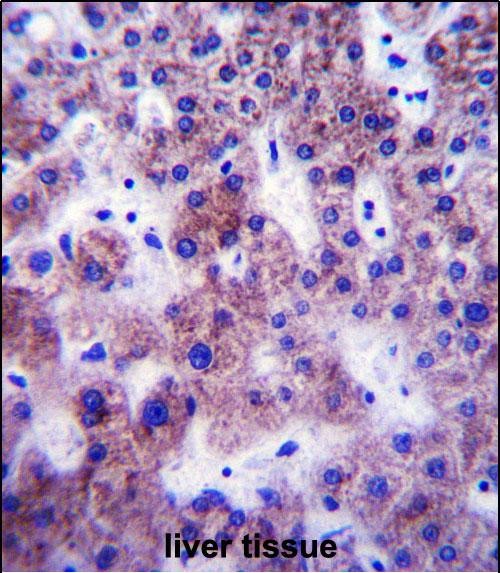
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1-1, UDPGT 1-1, UGT1*1, UGT1-01, UGT11, Bilirubin-specific UDPGT isozyme 1, hUG-BR1, UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1-A, UGT-1A, UGT1A, UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1, UGT1A1, GNT1, UGT1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 54658 |
| WB Predicted band size | 59.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This UGT1A1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 65-90 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human UGT1A1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于UGT1A1 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献的简要总结:
1. **文献名称**: "Characterization of UGT1A1 variants and their impact on drug metabolism"
**作者**: Strassburg CP, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用UGT1A1 (N-term)抗体通过Western blot分析不同基因突变(如UGT1A1*28)对酶表达水平的影响,发现某些突变导致蛋白表达显著降低,与伊立替康毒性相关。
2. **文献名称**: "Developmental expression of UGT1A1 in human liver"
**作者**: Miyagi SJ, Collier AC.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化及Western blot(使用N端特异性抗体),揭示了UGT1A1在胎儿和成人肝脏中的表达差异,表明其发育调控可能与新生儿黄疸相关。
3. **文献名称**: "UGT1A1 polymorphism-dependent pharmacokinetics of irinotecan in colorectal cancer patients"
**作者**: Innocenti F, et al.
**摘要**: 研究结合UGT1A1抗体检测肿瘤组织中酶的表达水平,发现UGT1A1低表达与患者接受伊立替康治疗后的严重中性粒细胞减少症风险增加相关。
注:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际文献需通过PubMed或学术数据库检索确认。若需具体文献,建议使用关键词“UGT1A1 antibody N-terminal”或“UGT1A1 Western blot”进一步查询。
The UGT1A1 (N-term) antibody is a specific immunological tool designed to detect the N-terminal region of the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 (UGT1A1) enzyme. UGT1A1. a member of the uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) superfamily, is primarily expressed in the liver and plays a critical role in phase II drug metabolism by conjugating glucuronic acid to lipophilic substrates, facilitating their excretion. It is particularly essential for the detoxification of bilirubin, and mutations in the UGT1A1 gene are linked to inherited disorders such as Crigler-Najjar syndrome and Gilbert’s syndrome, characterized by impaired bilirubin metabolism.
The N-terminal region of UGT1A1 is involved in substrate recognition and enzyme stability, making it a key target for functional studies. The UGT1A1 (N-term) antibody is commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess protein expression, localization, and tissue distribution. Researchers employ this antibody to investigate UGT1A1 regulation in liver diseases, drug-induced toxicity, or metabolic disorders, as well as to study genetic variants affecting enzyme activity. Its specificity helps distinguish UGT1A1 from other UGT isoforms, aiding in mechanistic studies of glucuronidation pathways. Additionally, this tool supports clinical research on personalized medicine, particularly in predicting drug responses or toxicity risks tied to UGT1A1 polymorphisms.
×