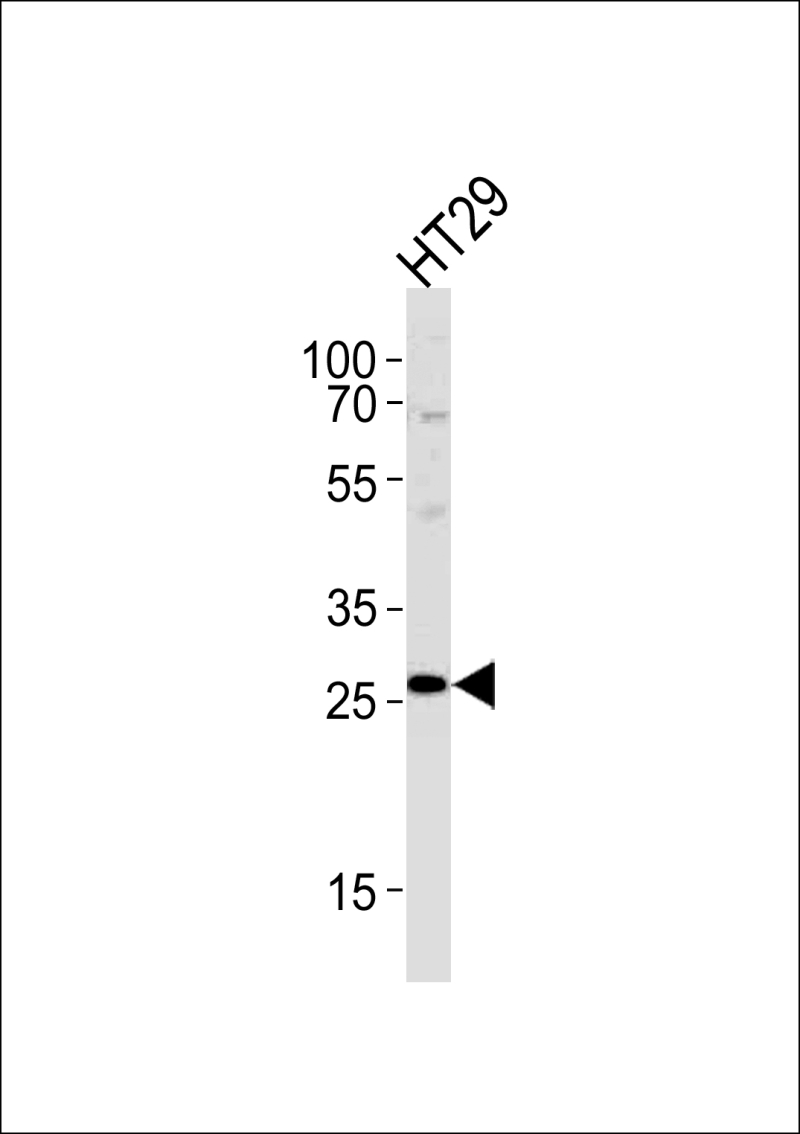
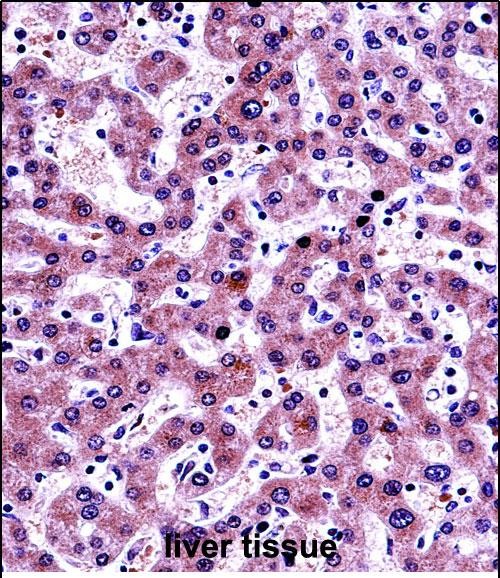
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase, NNMT |
| Entrez GeneID | 4837 |
| WB Predicted band size | 29.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This NNMT antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 101-130 amino acids from the Central region of human NNMT. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于NNMT抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**: "Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase enhances resistance to 5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer cells through inhibition of apoptosis"
**作者**: Pozzi V. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用NNMT抗体通过Western blot和免疫组化分析结直肠癌细胞中NNMT的表达,发现NNMT过表达通过抑制凋亡通路增强癌细胞对5-氟尿嘧啶的耐药性,提示NNMT可能作为化疗抵抗的生物标志物。
2. **文献名称**: "NNMT promotes cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer via modulating metabolism and DNA repair"
**作者**: Eckert M.A. et al.
**摘要**: 研究使用NNMT抗体检测卵巢癌组织中NNMT蛋白水平,发现其高表达与铂类化疗耐药相关。机制上,NNMT通过调节NAD+代谢和增强DNA修复能力促进肿瘤细胞存活。
3. **文献名称**: "Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase regulates hepatic lipid metabolism through SIRT1-mediated deacetylation"
**作者**: Hong S. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究采用NNMT抗体在小鼠肝脏组织中进行免疫沉淀分析,揭示NNMT通过抑制SIRT1去乙酰化活性影响脂质代谢,为代谢综合征和脂肪肝的治疗提供了新靶点。
以上研究均通过NNMT抗体在分子水平探究其功能,涵盖肿瘤耐药、代谢调控等方向。如需具体实验细节或更多文献,可进一步补充说明。
**Background of NNMT Antibody**
Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT) is a cytosolic enzyme that catalyzes the methylation of nicotinamide (vitamin B3) using S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) as a methyl donor, producing N-methylnicotinamide (MNA) and S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH). This reaction plays a role in regulating cellular methylation balance, NAD+ metabolism, and energy homeostasis. NNMT is implicated in diverse physiological and pathological processes, including cancer progression, obesity, diabetes, and neurodegenerative diseases. Its overexpression has been observed in multiple cancers, such as hepatocellular carcinoma, glioblastoma, and colorectal cancer, where it promotes tumor growth, metastasis, and chemoresistance by altering metabolic pathways and epigenetic regulation.
NNMT-specific antibodies are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in biological systems. These antibodies enable detection of NNMT protein levels via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF), aiding in biomarker discovery and mechanistic research. High-quality NNMT antibodies are validated for specificity, often through knockout controls or siRNA knockdown experiments. Researchers also utilize NNMT inhibitors or genetic models to explore therapeutic targeting of NNMT in diseases. However, challenges remain in standardizing assays due to NNMT's variable expression across tissues and its complex interplay with metabolic networks. Overall, NNMT antibodies are essential for advancing insights into its role in disease pathogenesis and potential as a therapeutic target.
×