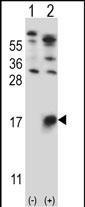
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
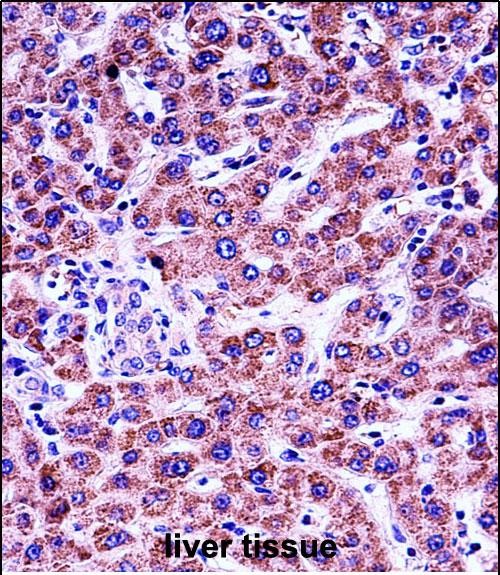
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Glycophorin-B, PAS-3, SS-active sialoglycoprotein, Sialoglycoprotein delta, CD235b, GYPB, GPB |
| Entrez GeneID | 2994 |
| WB Predicted band size | 9.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This GYPB antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 22-51 amino acids from the Central region of human GYPB. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GYPB抗体的3篇代表性文献信息及摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Glycophorin B as a molecular target in red blood cell membrane disorders*
**作者**:Reid ME, et al.
**摘要**:该文献探讨了GYPB在红细胞膜结构中的作用及其作为免疫原的机制,分析了GYPB抗体在溶血性输血反应和新生儿溶血病中的临床意义,强调其在MNS血型系统抗原变异中的关键性。
---
2. **文献名称**:*A novel anti-GYPB antibody causing hemolytic transfusion reaction: Case report and epitope characterization*
**作者**:Yamamoto F, et al.
**摘要**:报道一例由抗GYPB抗体引发的严重输血反应病例,通过分子生物学技术鉴定了抗体的特异性表位,揭示了GYPB基因突变(如c.230C>T)导致的抗原变异与抗体产生的关联。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Development of a high-throughput genotyping assay for GYPB variants associated with anti-"Mia" immunization*
**作者**:Huang CH, et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种基于PCR的快速分型技术,用于检测与GYPB抗体(如抗-Mur)相关的基因多态性,为预防亚洲人群高发的抗GYPB相关输血并发症提供了筛查策略。
---
**补充说明**:
GYPB抗体多针对MNS血型系统的Mur抗原(如抗-Mur),在亚洲人群输血反应中较常见。上述文献涵盖基础机制、临床案例及检测技术,可为输血医学研究提供参考。如需具体年份或期刊信息,可进一步补充检索。
×