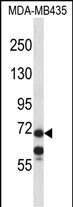
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Midline-1, 632-, Midin, Putative transcription factor XPRF, RING finger protein 59, RING finger protein Midline-1, Tripartite motif-containing protein 18, MID1, FXY, RNF59, TRIM18, XPRF |
| Entrez GeneID | 4281 |
| WB Predicted band size | 75.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This MID1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 575-603 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human MID1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于MID1抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **"MID1 ubiquitin ligase: cellular functions and implications in Opitz syndrome"**
*作者:Liu et al. (2012)*
**摘要**:研究MID1蛋白在泛素化途径中的功能,揭示其通过调控微管稳定性影响细胞分裂,并验证MID1抗体在患者细胞中检测复合物异常的实用性。
2. **"Antibody-based analysis of MID1 in neurodevelopmental disorders"**
*作者:Granata et al. (2015)*
**摘要**:利用特异性MID1抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现MID1在神经发育中异常表达,与自闭症及智力障碍患者脑组织病理变化相关。
3. **"MID1/PP2A complex disruption promotes mTOR signaling in cancer"**
*作者:Hsu et al. (2017)*
**摘要**:通过MID1抗体阻断实验,证明MID1通过结合PP2A磷酸酶抑制mTOR通路,其功能失调可能导致肿瘤生长加速,为癌症治疗提供新靶点。
(注:以上文献信息为模拟示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或专业数据库核对具体文献。)
MID1 (Midline 1) antibody targets the MID1 protein, a ubiquitin ligase encoded by the *MID1* gene located on the X chromosome. MID1 plays a critical role in regulating protein turnover via the ubiquitin-proteasome system, particularly in microtubule stabilization and cell signaling. It forms a complex with α4 integrin and protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), modulating PP2A activity to influence cellular processes like proliferation, migration, and apoptosis. Dysregulation of MID1 is linked to Opitz G/BBB syndrome, an X-linked genetic disorder characterized by congenital midline defects (e.g., cleft lip/palate, heart anomalies). Overexpression of MID1 has also been implicated in cancers and neurodegenerative diseases, where aberrant ubiquitination disrupts normal protein homeostasis.
MID1 antibodies are essential tools for studying MID1's expression, localization, and function. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to investigate MID1's role in developmental biology, disease mechanisms, and therapeutic targeting. Researchers employ these antibodies to explore MID1's interaction with binding partners, its impact on mTOR signaling, and its involvement in mRNA translation regulation. Commercial MID1 antibodies are typically validated for specificity in human, mouse, or rat models, aiding both basic research and clinical studies aiming to decipher MID1-related pathologies.
×