| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
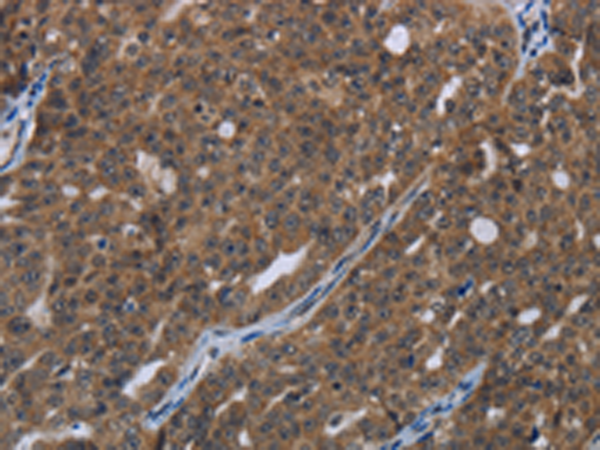
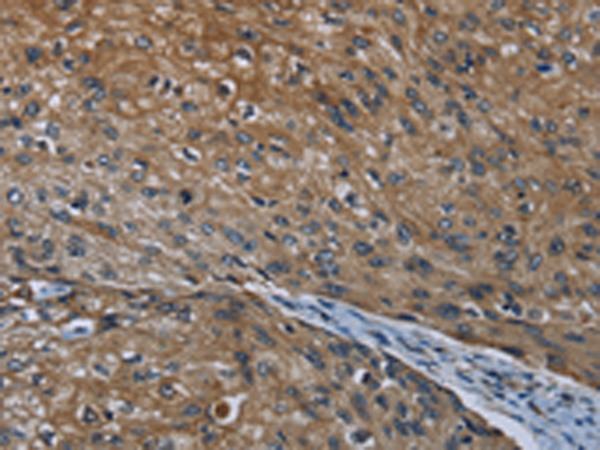
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HOX3, HOX3A |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human HOXC8 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MORN1 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献的简要总结:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Toxoplasma gondii MORN1 is required for proper assembly of the basal complex during cell division"*
**作者**: Heaslip, A.T., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过使用MORN1的N端抗体,发现弓形虫中MORN1蛋白在细胞分裂过程中对基底复合体的组装至关重要。免疫荧光实验显示MORN1定位于子代寄生虫的基底环,敲除MORN1导致分裂缺陷。
2. **文献名称**: *"The Toxoplasma gondii centrosome is the platform for internal daughter budding as revealed by a N-terminally tagged MORN1 protein"*
**作者**: Chen, C.T., et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用N端特异性抗体和标记技术,证实MORN1在弓形虫中心体周围富集,并参与子代寄生虫内芽殖的早期阶段。抗体染色显示MORN1在分裂过程中动态定位。
3. **文献名称**: *"Plasmodium falciparum MORN1 regulates the organization and segregation of apical organelles during schizogony"*
**作者**: Kono, M., et al.
**摘要**: 通过MORN1的N端抗体进行免疫定位,研究发现疟原虫中MORN1调控顶端细胞器(如棒状体和微线体)的分裂和分配,缺失MORN1会破坏裂殖体的正常发育。
---
以上文献均通过MORN1的N端抗体进行蛋白定位或功能研究,聚焦于顶复门寄生虫(如弓形虫、疟原虫)的细胞分裂机制。如需具体文献来源,可进一步通过PubMed或SciHub检索标题及作者获取全文。
The MORN1 (Membrane Occupation and Recognition Nexus) antibody targets the N-terminal region of the MORN1 protein, a conserved protein containing multiple MORN (Membrane Occupation and Recognition Nexus) motifs. These motifs are implicated in membrane binding and protein-protein interactions. MORN1 is notably studied in apicomplexan parasites, such as *Plasmodium* (malaria-causing pathogens) and *Toxoplasma gondii*, where it plays critical roles in cell division, formation of inner membrane complexes, and host cell invasion. The protein localizes to dynamic cytoskeletal structures, including the basal complex, and is essential for maintaining parasite structural integrity and replication.
The MORN1 (N-term) antibody is widely used in research to detect endogenous MORN1 expression and track its subcellular localization via techniques like immunofluorescence, Western blotting, or immunoprecipitation. Its specificity for the N-terminal region helps distinguish MORN1 from other MORN-containing proteins. Studies leveraging this antibody have advanced understanding of apicomplexan cell biology, particularly in elucidating mechanisms of parasite proliferation, organelle biogenesis, and host-pathogen interactions. It also serves as a tool for exploring MORN1's potential roles in non-parasitic organisms, where the protein's function remains less characterized. The antibody's utility underscores its importance in both basic parasitology research and drug target discovery for diseases like malaria and toxoplasmosis.
×