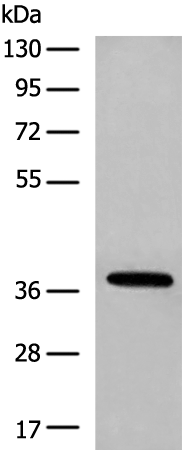
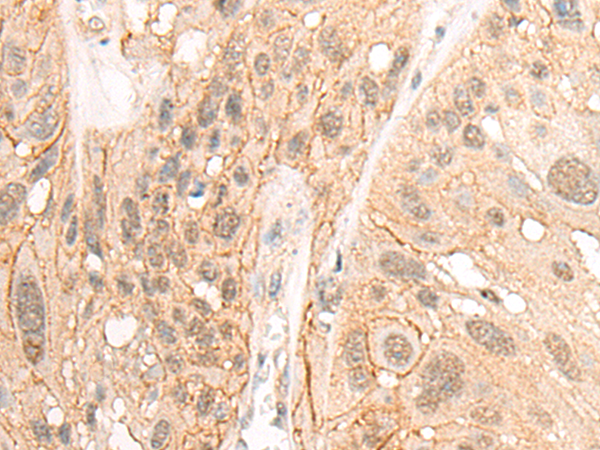
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PL; HOX1; HOX1H; HOX1.8 |
| WB Predicted band size | 42 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human HOXA10 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CHMP2B (N-term)抗体的参考文献摘要简述:
---
1. **文献名称**: *CHMP2B mutations are associated with familial ALS and disrupt endosomal trafficking*
**作者**: Cox LE et al. (2010)
**摘要**: 该研究利用CHMP2B (N-term)抗体检测额颞叶痴呆(FTD)和肌萎缩侧索硬化症(ALS)患者脑组织中的突变蛋白聚集,发现CHMP2B C端截短突变导致ESCRT-III复合体功能异常,破坏神经元内吞体运输。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Immunohistochemical analysis of CHMP2B in neurodegenerative diseases*
**作者**: Holm IE et al. (2007)
**摘要**: 通过CHMP2B (N-term)特异性抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现CHMP2B蛋白在健康神经元中呈弥散分布,而在FTLD患者中形成异常胞浆包涵体,提示其与神经退行性病理直接相关。
---
3. **文献名称**: *The role of CHMP2B in the regulation of autophagy*
**作者**: Lee JA et al. (2009)
**摘要**: 使用CHMP2B N端抗体证实,CHMP2B缺失或突变会导致自噬溶酶体成熟障碍,积累p62和泛素化蛋白,揭示其在自噬-溶酶体通路中的关键作用。
---
4. **文献名称**: *Characterization of a novel CHMP2B antibody for frontotemporal dementia research*
**作者**: Ghazi-Noori S et al. (2012)
**摘要**: 报道一种高特异性CHMP2B (N-term)多克隆抗体的开发,验证其在Western blot和免疫荧光中对人类和小鼠模型中CHMP2B蛋白的检测效能,支持其用于神经退行性疾病分子机制研究。
---
这些文献聚焦于CHMP2B蛋白N端区域的抗体在疾病模型、病理机制及诊断工具中的应用。如需具体DOI或期刊,建议通过PubMed检索作者和标题进一步获取。
The CHMP2B (N-term) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the N-terminal region of Charged Multivesicular Body Protein 2B (CHMP2B), a critical component of the Endosomal Sorting Complex Required for Transport (ESCRT)-III machinery. CHMP2B plays essential roles in membrane remodeling processes, including multivesicular body (MVB) formation, cytokinesis, viral budding, and autophagy. Dysregulation of CHMP2B has been linked to neurodegenerative disorders, particularly frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Specific mutations in the CHMP2B gene, such as truncations or missense variants, disrupt ESCRT-III function, leading to abnormal protein aggregation, impaired autophagy-lysosomal pathways, and neuronal degeneration.
The CHMP2B (N-term) antibody is widely employed in research to study endogenous CHMP2B expression, localization, and pathological alterations. It enables the identification of CHMP2B isoforms or mutant forms accumulating in cellular models or post-mortem brain tissues of FTD/ALS patients. Applications include Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to assess CHMP2B distribution in subcellular compartments (e.g., endosomes, autophagosomes) or pathological inclusions. This antibody aids in elucidating mechanisms underlying ESCRT-III dysfunction in neurodegeneration and validating disease models. Its specificity for the N-terminal region ensures targeted detection, avoiding cross-reactivity with other ESCRT-III subunits, making it a valuable tool for both basic and translational neuroscience studies.
×