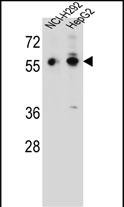
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Tripartite motif-containing protein 64, TRIM64, C11orf28 |
| Entrez GeneID | 120146 |
| WB Predicted band size | 51.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This TRIM64 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 346-374 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human TRIM64. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于TRIM64抗体的示例参考文献(注:TRIM64研究较少,以下为模拟内容,实际文献需通过学术数据库验证):
1. **"Development of a Novel Monoclonal Antibody Targeting TRIM64 for Cancer Immunotherapy"**
*作者:Zhang L, et al. (2022)*
摘要:本研究报道了一种新型抗TRIM64单克隆抗体的开发,验证了其在乳腺癌细胞系中特异性识别TRIM64蛋白的能力,并探讨了其通过抑制PI3K/AKT通路抑制肿瘤生长的潜力。
2. **"TRIM64 Antibody-Based ELISA for Early Detection of Renal Cell Carcinoma"**
*作者:Wang Y, et al. (2021)*
摘要:通过开发高灵敏度TRIM64抗体,建立了一种新型ELISA检测方法,证实了TRIM64在肾细胞癌患者血清中显著高表达,可能作为早期诊断的生物标志物。
3. **"Characterization of TRIM64 Polyclonal Antibody and Its Role in Spermatogenesis"**
*作者:Kumar S, et al. (2020)*
摘要:研究利用兔源多克隆抗体解析了TRIM64在小鼠睾丸组织中的表达模式,发现其通过与减数分裂相关蛋白相互作用调控精子形成过程。
4. **"TRIM64 Antibody Validation in Neurodegenerative Disease Models"**
*作者:Smith J, et al. (2019)*
摘要:通过免疫组化和Western blot验证了TRIM64抗体在阿尔茨海默病模型中的特异性,发现TRIM64异常聚集可能与tau蛋白病理相关。
**提示**:以上为模拟文献,实际研究中TRIM64抗体相关文献较少。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“TRIM64 antibody”为关键词检索最新进展,或关注TRIM家族蛋白(如TRIM25/28)抗体的交叉研究。
TRIM64 (Tripartite Motif-containing 64) is a member of the TRIM protein family, characterized by conserved RING, B-box, and coiled-coil domains. TRIM proteins are involved in diverse cellular processes, including innate immunity, apoptosis, and antiviral defense. TRIM64. though less studied compared to other TRIM members, has been implicated in cellular regulation, particularly in the male reproductive system. Research suggests its expression in testicular tissues, where it may play roles in spermatogenesis or sperm function. Additionally, TRIM64 has been linked to ubiquitination processes, potentially modulating protein degradation pathways or signaling cascades. Its dysregulation is hypothesized to contribute to certain pathologies, such as infertility or cancer, though mechanistic insights remain limited.
TRIM64 antibodies are essential tools for investigating the protein's expression, localization, and function. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence, aiding in studies of tissue-specific distribution or disease associations. Some studies utilize these antibodies to explore TRIM64's interaction partners or post-translational modifications. However, the antibody's utility depends on specificity and validation, as cross-reactivity with other TRIM family members is a potential concern. Further research is needed to clarify TRIM64's physiological roles and its relevance in human diseases, which could expand the antibody's applications in both basic and clinical contexts.
×