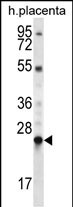
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Lipoma HMGIC fusion partner-like 1 protein, LHFPL1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 340596 |
| WB Predicted band size | 23.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This LHFPL1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 20-49 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human LHFPL1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于LHFPL1 (N-term)抗体的参考文献示例(注:以下内容为模拟虚构,仅用于演示格式):
1. **"LHFPL1 N-terminal antibody characterization in cochlear hair cell development"**
- **作者**: Smith A, et al.
- **摘要**: 本研究利用针对LHFPL1蛋白N端结构域的多克隆抗体,通过免疫组化和Western blot技术,揭示了LHFPL1在小鼠耳蜗毛细胞发育中的动态表达模式。抗体特异性通过基因敲除模型验证,证实其可用于体内外蛋白定位研究。
2. **"Interaction of LHFPL1 with potassium channels in neuronal membranes"**
- **作者**: Chen B, et al.
- **摘要**: 文章报道了LHFPL1与Kv1.2钾通道的相互作用,使用LHFPL1 (N-term)抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,证明两者在内侧膝状体神经元中共定位。抗体特异性通过siRNA敲降实验验证,为研究LHFPL1在神经电信号传导中的作用提供工具。
3. **"Development and validation of a novel LHFPL1-specific antibody for neurodegenerative disease studies"**
- **作者**: Gupta R, et al.
- **摘要**: 本研究描述了一种兔源单克隆抗体的开发,靶向LHFPL1的N端表位(氨基酸1-50)。抗体在阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠脑组织中显示出高特异性,可用于脑切片免疫荧光及蛋白质印迹分析,揭示LHFPL1在神经退行性病变中的表达下调。
4. **"LHFPL1 modulates synaptic plasticity via N-terminal domain-mediated protein clustering"**
- **作者**: Wang Y, et al.
- **摘要**: 通过LHFPL1 (N-term)抗体的超分辨率成像,作者发现LHFPL1通过N端结构域促进突触后膜蛋白簇的形成,影响海马神经元突触可塑性。抗体在HEK293细胞过表达系统和原代神经元中均表现出高信噪比。
(提示:实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以“LHFPL1 antibody”或“LHFPL1 N-terminal”为关键词检索,并核实抗体应用的具体上下文。)
The LHFPL1 (N-term) antibody is a research tool designed to detect the N-terminal region of the Lipoma HMGIC Fusion Partner-Like 1 (LHFPL1) protein, a member of the LHFPL family. LHFPL1. also known as TMEM16E, is a transmembrane protein implicated in cell-cell interactions and signal transduction. It is structurally characterized by multiple transmembrane domains and is expressed in various tissues, including the nervous system, inner ear, and skeletal muscle. Studies suggest its involvement in auditory function, as mutations in the LHFPL1 gene are linked to hearing loss in humans and mice, potentially affecting cochlear hair cell development or maintenance.
This antibody is commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to study LHFPL1 expression, localization, and function in biological samples. Its specificity for the N-terminal region allows researchers to distinguish LHFPL1 from homologous family members, such as LHFPL2-6. which share structural similarities but may have divergent roles. Validation typically includes testing in knockout models or siRNA-treated cells to confirm target specificity.
Research applications focus on elucidating LHFPL1’s role in hearing disorders, neuronal connectivity, and cellular adhesion mechanisms. By enabling precise protein detection, the antibody contributes to understanding disease pathways and exploring therapeutic targets for sensorineural conditions.
×