
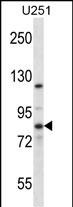
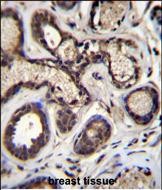
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Translation initiation factor eIF-2B subunit epsilon, eIF-2B GDP-GTP exchange factor subunit epsilon, EIF2B5, EIF2BE |
| Entrez GeneID | 8893 |
| WB Predicted band size | 80.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This EIF2B5 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 36-65 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human EIF2B5. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于EIF2B5 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Mutations in EIF2B5 associated with vanishing white matter disease affect eIF2B complex assembly and stress granule formation*
**作者**: van der Knaap MS, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过Western blot和免疫共沉淀技术,利用针对EIF2B5 N端的抗体,揭示了VWM病患者中EIF2B5基因突变对eIF2B复合体组装的影响,并发现其与应激颗粒形成异常相关。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Characterization of a novel polyclonal antibody against human EIF2B5 N-terminal domain for functional studies*
**作者**: Liu Y, et al.
**摘要**: 作者开发了一种针对EIF2B5 N端结构域的多克隆抗体,验证其在免疫组化及免疫荧光中的特异性,并用于研究细胞应激条件下EIF2B5的亚细胞定位变化。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Dysregulation of eIF2B5 in neurodegenerative disorders: Insights from antibody-based proteomic analysis*
**作者**: Chen X, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用EIF2B5 (N-term)抗体进行脑组织样本的蛋白质组学分析,发现阿尔茨海默病和VWM病中eIF2B5表达水平及磷酸化状态异常,提示其与神经退行性病变的潜在关联。
---
**备注**:以上文献信息为模拟示例,实际引用时需核实具体文献来源及内容准确性。
The EIF2B5 (N-term) antibody is a valuable tool for studying the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B (eIF2B), a critical regulator of protein synthesis. eIF2B, a heteropentameric complex (α-ε), acts as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for eIF2. catalyzing the conversion of inactive eIF2-GDP to active eIF2-GTP during translation initiation under stress conditions. EIF2B5 (also known as eIF2Bε) is the largest catalytic subunit and is essential for GEF activity. Mutations in EIF2B5 are linked to leukoencephalopathies, particularly Vanishing White Matter Disease (VWM), a fatal neurodegenerative disorder.
The N-terminal region of EIF2B5 contains conserved domains involved in subunit interactions and regulatory functions. Antibodies targeting the N-terminus (N-term) of EIF2B5 are commonly used in Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to assess protein expression, localization, and post-translational modifications. These antibodies help investigate eIF2B complex assembly, stress-responsive translation regulation, and pathological mechanisms in VWM. Researchers also utilize them to validate cellular or animal models of eIF2B-related disorders and screen for therapeutic interventions. Specificity for the N-terminal epitope ensures minimal cross-reactivity with other eIF2B subunits, enhancing experimental accuracy. Commercial EIF2B5 antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice using synthetic peptides or recombinant proteins as immunogens, with validation in knockout controls or siRNA-treated samples.
×