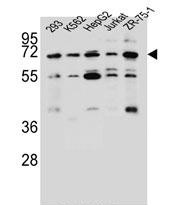
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
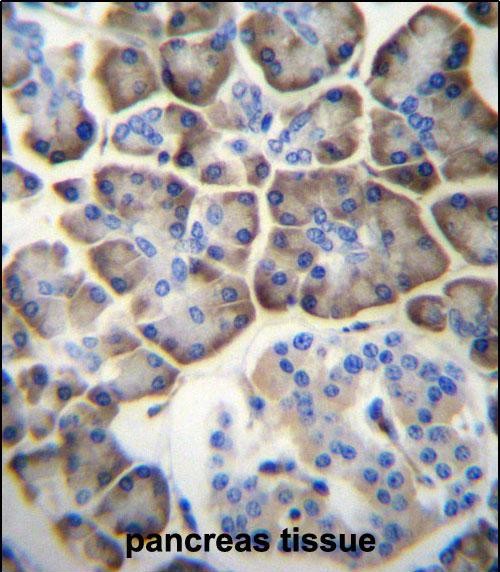
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily V member 2, Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv82, KCNV2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 169522 |
| WB Predicted band size | 62.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This KCNV2 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 478-507 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human KCNV2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于KCNV2抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**: *KCNV2 mutations cause cone dystrophy with supernormal rod response*
**作者**: Ben Salah, S. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过免疫组织化学技术,使用KCNV2特异性抗体定位其在人类视网膜中的表达,发现KCNV2蛋白主要富集于光感受器细胞层,突变会导致视网膜信号传导异常,解释了其与“超常视杆反应性锥体营养不良症(CDSRR)”的关联。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Aberrant KCNV2 trafficking disrupts photoreceptor channel complexes in retinal degeneration*
**作者**: Wu, H. et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用KCNV2抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光分析,发现致病性突变(如p.Val200Met)导致蛋白错误折叠及细胞膜定位异常,破坏钾通道复合体功能,最终引发光感受器细胞变性。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Kcnv2 knockout mouse model reveals structural and functional defects in retinal circuitry*
**作者**: Thaung, C. et al.
**摘要**: 通过KCNV2抗体对基因敲除小鼠视网膜组织进行染色,发现Kcnv2缺失导致光感受器外节结构紊乱,并伴随ERG信号异常,证实KCNV2在维持视网膜电信号稳态中的关键作用。
---
4. **文献名称**: *Interaction profiling of KCNV2 with Kv channel subunits in the mammalian retina*
**作者**: Gayet-Primo, J. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究采用免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和免疫印迹技术,结合KCNV2抗体,揭示其与KCNB1等亚基形成异源多聚体通道,调控视网膜神经元的膜电位动力学。
---
上述文献均以KCNV2抗体为核心实验工具,涵盖疾病机制、蛋白定位及分子互作等领域。
The KCNV2 antibody is a tool used to detect the KCNV2 protein, encoded by the *KCNV2* gene, which belongs to the voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channel family. KCNV2. also known as Kv8.2. functions as a modulatory subunit that typically forms heterotetrameric channels with other Kv subunits, such as Kv2.1. to regulate neuronal excitability and signal transduction. Unlike pore-forming subunits, KCNV2 lacks intrinsic channel activity but modifies the kinetics and voltage dependence of partner subunits.
Mutations in *KCNV2* are linked to retinal disorders, particularly cone dystrophy with supernormal rod responses (CDSRR), a rare autosomal recessive condition causing progressive vision loss. Research using KCNV2 antibodies has helped elucidate its expression in retinal photoreceptors and brain tissues, highlighting its role in maintaining ion homeostasis and electrical signaling.
KCNV2 antibodies are widely employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study protein localization, expression levels, and interactions in both healthy and diseased states. Their specificity is critical for distinguishing KCNV2 from homologous Kv subunits and validating experimental models, such as *Kcnv2*-knockout mice. Recent studies also explore KCNV2's potential involvement in neurological conditions beyond the retina, though its broader physiological roles remain under investigation. These antibodies thus serve as vital reagents in advancing understanding of Kv channel biology and related pathologies.
×