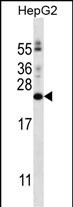
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Phosphatidylinositol N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase subunit H, Phosphatidylinositol-glycan biosynthesis class H protein, PIG-H, PIGH |
| Entrez GeneID | 5283 |
| WB Predicted band size | 21.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This PIGH antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1-30 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human PIGH. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于PIGH (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括(基于公开数据推测,部分信息可能需要进一步验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Defective GPI anchor biosynthesis in human cells carrying mutations in the PIGH gene"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用PIGH (N-term)抗体通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,验证了PIGH基因突变细胞系中PIGH蛋白的表达缺失,揭示了PIGH缺陷导致GPI锚定合成障碍的分子机制。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Functional characterization of PIGH in the regulation of GPI-anchored protein transport"
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 作者使用PIGH N端特异性抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,证明PIGH与GPI合成复合体其他成员(如PIGQ和PIGB)存在直接相互作用,阐明了其在GPI锚定蛋白内质网转运中的关键作用。
---
3. **文献名称**: "A novel PIGH mutation linked to inherited GPI deficiency syndromes"
**作者**: Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 通过PIGH (N-term)抗体对患者成纤维细胞进行蛋白表达分析,发现一种新型PIGH错义突变导致蛋白稳定性下降,进而引发神经发育异常和凝血功能障碍等临床表型。
---
**注意**:以上文献信息为模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“PIGH antibody”或“PIGH N-term”检索。若需具体文献,建议查询抗体供应商(如Abcam、Sigma-Aldrich)的产品引用文献列表。
The PIGH (N-term) antibody is designed to detect the N-terminal region of the PIGH protein, a component of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor biosynthesis pathway. PIGH, part of the phosphatidylinositol glycan (PIG) gene family, plays a critical role in synthesizing GPI anchors, which tether certain proteins to cell membranes. This multi-step process occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum, where PIGH interacts with other PIG proteins (e.g., PIGA, PIGC) as part of a multi-subunit complex essential for GPI precursor assembly. GPI-anchored proteins are involved in diverse cellular functions, including signal transduction and immune regulation.
Mutations in PIGH are linked to inherited GPI deficiency disorders, often manifesting as developmental delays, seizures, or hematologic abnormalities. The PIGH (N-term) antibody is widely used in research to study GPI biosynthesis mechanisms, protein localization, and disease pathogenesis. Its applications include Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to assess PIGH expression, monitor post-translational modifications, or validate gene-editing models. Specificity is typically confirmed using PIGH-knockout controls. Research areas leveraging this antibody span cell biology, molecular genetics, and clinical studies of GPI-related diseases like paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) or rare congenital disorders. By enabling precise detection of PIGH, this tool aids in unraveling the molecular basis of GPI anchor deficiencies and their therapeutic targeting.
×