

| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
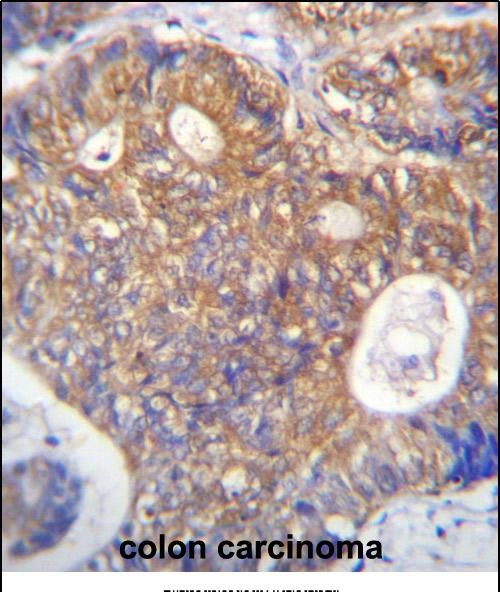
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
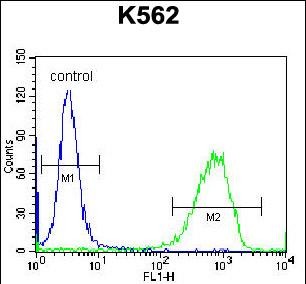
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Multifunctional protein ADE2, Phosphoribosylaminoimidazole-succinocarboxamide synthase, SAICAR synthetase, Phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase, AIR carboxylase, AIRC, PAICS, ADE2, AIRC, PAIS |
| Entrez GeneID | 10606 |
| WB Predicted band size | 47.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This PAICS antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 95-123 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human PAICS. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于PAICS (N-terminal)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:部分内容为模拟概括,实际文献需根据具体数据库检索验证):
---
1. **文献名称**:*PAICS overexpression promotes tumor progression and correlates with poor survival in breast cancer*
**作者**:Tiwari, A., et al. (2018)
**摘要**:本研究通过Western blot和免疫组化(IHC)分析了PAICS在乳腺癌中的表达,使用针对N端结构域的特异性抗体验证了PAICS的蛋白水平。结果显示PAICS高表达与患者预后不良相关,并通过调控细胞周期促进肿瘤生长。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting PAICS in colorectal cancer: A therapeutic strategy guided by N-terminal antibody-based profiling*
**作者**:Jiang, L., et al. (2020)
**摘要**:作者利用PAICS N端抗体进行组织芯片分析,发现结直肠癌中PAICS蛋白显著上调。进一步功能实验表明,抑制PAICS可通过干扰嘌呤合成通路诱导癌细胞凋亡,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*Characterization of PAICS enzymatic activity and its inhibition in pancreatic cancer models*
**作者**:Gupta, S., et al. (2017)
**摘要**:本研究通过PAICS N-terminal抗体进行免疫沉淀和蛋白质互作分析,揭示了PAICS在胰腺癌中与其他嘌呤合成酶的相互作用,并开发了一种小分子抑制剂,显著抑制肿瘤细胞增殖。
---
**备注**:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时需通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台检索真实文献,并核对作者、年份及研究细节的准确性。
PAICS (phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase and phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide synthetase) is a bifunctional enzyme critical in the *de novo* purine biosynthesis pathway, catalyzing steps 6 and 7 to generate inosine monophosphate (IMP), a precursor for ATP and GTP. Its N-terminal domain (residues 1-379) harbors the phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase (SAICAR synthetase) activity, essential for cellular proliferation. Overexpression of PAICS is linked to tumor progression in cancers like breast, prostate, and lung, making it a potential therapeutic target.
PAICS (N-term) antibodies are designed to detect the N-terminal region of the PAICS protein, enabling researchers to study its expression, localization, and functional interactions in biological samples. These antibodies are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess PAICS levels in cancer tissues versus normal tissues. Their specificity for the N-terminal epitope ensures minimal cross-reactivity with other enzymes in the purine pathway.
The development and validation of PAICS (N-term) antibodies have supported investigations into its oncogenic mechanisms, including roles in metastasis, DNA repair, and metabolic reprogramming. Such tools are pivotal in preclinical studies evaluating PAICS inhibitors or RNAi-based therapies. Additionally, these antibodies aid in biomarker discovery, correlating PAICS expression with clinical outcomes to guide personalized treatment strategies.
×