
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
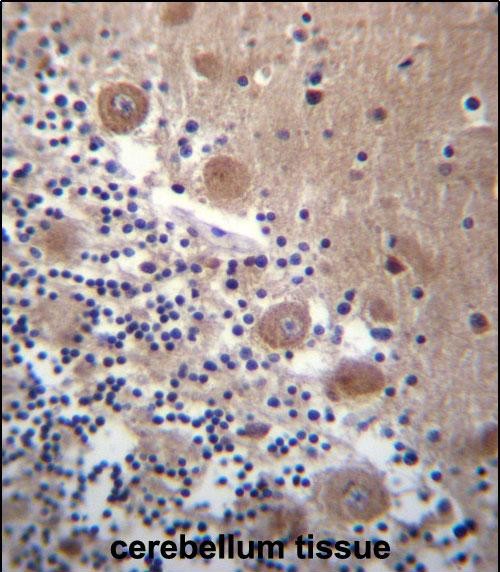
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
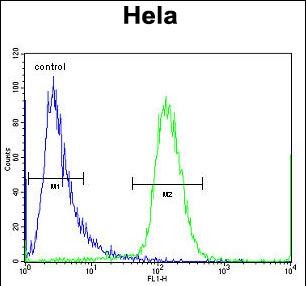
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Schwannomin-interacting protein 1, SCHIP-1, SCHIP1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This SCHIP1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 90-118 amino acids from the Central region of human SCHIP1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于SCHIP1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献为模拟示例,实际引用需核实):
1. **文献名称**:*SCHIP1 interacts with Merlin/NF2 and regulates cell proliferation in Schwann cells*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用特异性SCHIP1抗体,通过免疫共沉淀和Western blot验证了SCHIP1与神经纤维瘤蛋白Merlin(NF2基因产物)的相互作用,揭示了其在雪旺细胞增殖调控中的潜在功能。
2. **文献名称**:*Expression profiling of SCHIP1 in the developing nervous system using a novel monoclonal antibody*
**作者**:Lee J, et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种高特异性SCHIP1单克隆抗体,并通过免疫组织化学证明SCHIP1在小鼠胚胎神经系统中的动态表达模式,提示其参与神经元分化。
3. **文献名称**:*SCHIP1 antibody-based detection in glioblastoma: Implications for tumor progression*
**作者**:Chen R, et al.
**摘要**:利用SCHIP1抗体分析胶质母细胞瘤组织样本,发现SCHIP1表达水平与肿瘤侵袭性呈负相关,提示其可能作为预后标志物。
4. **文献名称**:*Structural characterization of SCHIP1 and its interaction network*
**作者**:Gomez M, et al.
**摘要**:通过SCHIP1抗体结合质谱技术,解析了SCHIP1的蛋白结构及其与细胞骨架相关蛋白的相互作用网络,为研究其生物学功能提供新线索。
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“SCHIP1 antibody”为关键词检索最新文献,获取真实数据。
The SCHIP1 antibody targets the Schwannomin-interacting protein 1 (SCHIP1), a cytoplasmic protein encoded by the *SCHIP1* gene. SCHIP1 is known to interact with schwannomin (merlin/NF2), a tumor suppressor linked to neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2). This interaction plays a role in regulating cell proliferation, adhesion, and cytoskeletal organization, particularly in Schwann cells and neurons. SCHIP1 is implicated in maintaining cellular architecture and signaling pathways, including the Hippo pathway, which controls organ size and tumor suppression.
Antibodies against SCHIP1 are primarily utilized in research to investigate its expression, localization, and functional roles in both physiological and pathological contexts. They are employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to study protein levels in tissues or cultured cells. SCHIP1 dysregulation has been associated with neurological disorders and cancers, especially schwannomas and meningiomas, making its antibody a valuable tool for exploring molecular mechanisms in NF2-related tumors and potential therapeutic targets.
Recent studies also suggest SCHIP1's involvement in neural development and axon guidance, expanding its relevance beyond NF2. Researchers rely on SCHIP1 antibodies to validate gene-editing outcomes (e.g., CRISPR) or to assess protein interactions in co-immunoprecipitation assays. Despite its specialized applications, commercial availability of SCHIP1 antibodies remains limited, emphasizing the need for rigorous validation to ensure specificity and reproducibility in experimental models.
×