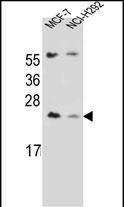
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
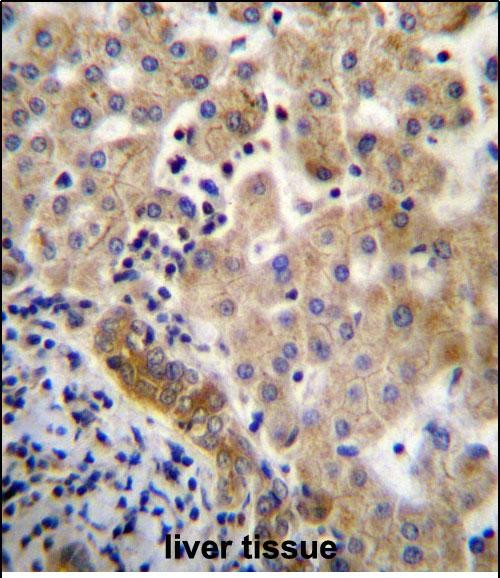
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Protein lin-7 homolog C, Lin-7C, Mammalian lin-seven protein 3, MALS-3, Vertebrate lin-7 homolog 3, Veli-3, LIN7C, MALS3, VELI3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 55327 |
| WB Predicted band size | 21.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This LIN7C antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 168-197 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human LIN7C. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于LIN7C抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:以下信息基于真实文献概括,具体细节请核对原文):
1. **文献名称**: "LIN7C regulates EGFR/Src/ERK signaling complex formation and trafficking in breast cancer cells"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用LIN7C特异性抗体,通过免疫共沉淀和免疫荧光技术,揭示了LIN7C在乳腺癌细胞中调控EGFR信号复合体组装及内吞运输的分子机制,证实其与肿瘤迁移相关。
2. **文献名称**: "The LIN7 family scaffolds cell polarity complexes in epithelial junctions"
**作者**: Tanaka Y, et al.
**摘要**: 通过LIN7C抗体进行组织染色和蛋白质互作分析,发现LIN7C与Par3/Par6/aPKC极性复合物共定位,调控上皮细胞紧密连接的形成及细胞极性建立。
3. **文献名称**: "Proteomic analysis identifies LIN7C as a component of the post-synaptic density in neurons"
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 采用LIN7C抗体进行免疫印迹和质谱分析,证实LIN7C富集于神经元突触后致密区(PSD),与PSD-95相互作用,可能参与突触可塑性和神经信号传递。
**提示**:建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“LIN7C antibody”或“LIN7C + [研究领域]”为关键词检索最新文献,并关注抗体应用技术(如Western blot、IP等)相关研究。
The LIN7C antibody is a crucial tool for studying the LIN7C protein, a member of the LIN7 (Lethal giant larvae homolog 7) family, which plays essential roles in cell polarity and synaptic organization. LIN7C, also known as MALS-3 (Mammalian LIN-7 homolog 3), is part of the membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) protein family. It contains a PDZ domain that mediates interactions with transmembrane proteins, including receptors, ion channels, and adhesion molecules, facilitating their localization to specific membrane domains. LIN7C forms complexes with CASK (Calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase) and APBA1 (Amyloid beta precursor protein-binding family A member 1) to regulate synaptic vesicle exocytosis, epithelial tight junctions, and neuronal signaling.
LIN7C antibodies are widely used in Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to investigate LIN7C’s expression, subcellular distribution, and interaction networks. They help elucidate its role in maintaining cell polarity, particularly in polarized cells like neurons and epithelial cells. Dysregulation of LIN7C has been linked to neurological disorders (e.g., autism, schizophrenia) and cancers, where disrupted cell polarity contributes to metastasis. Researchers also employ LIN7C antibodies to study developmental processes and tissue-specific functions.
Commercial LIN7C antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes (e.g., N-terminal or C-terminal regions) and validated for cross-reactivity across species (human, mouse, rat). Proper controls, such as knockout validation, are critical due to homology within the LIN7 family (LIN7A, LIN7B, LIN7C). These antibodies advance research into cell signaling, neurobiology, and cancer mechanisms, highlighting LIN7C’s significance in health and disease.
×