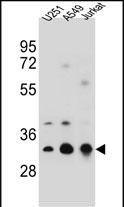
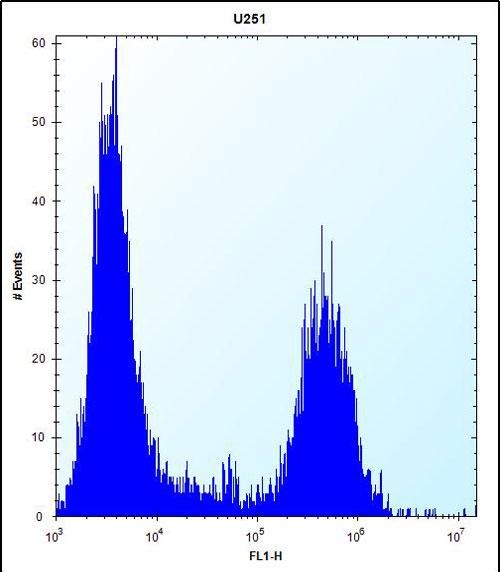
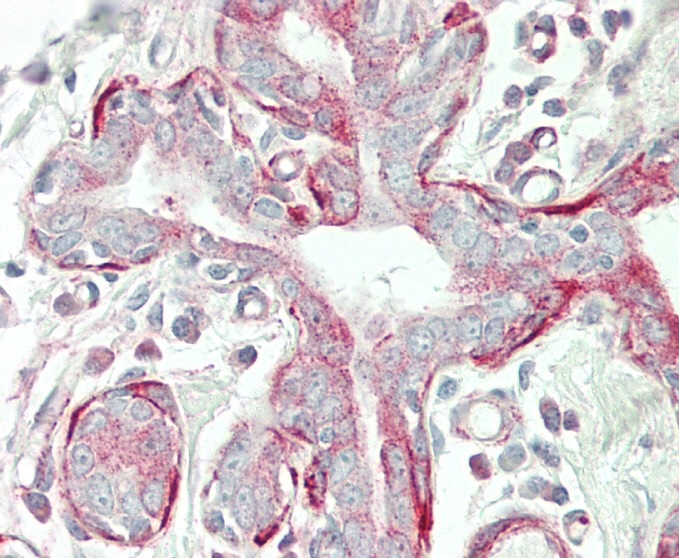
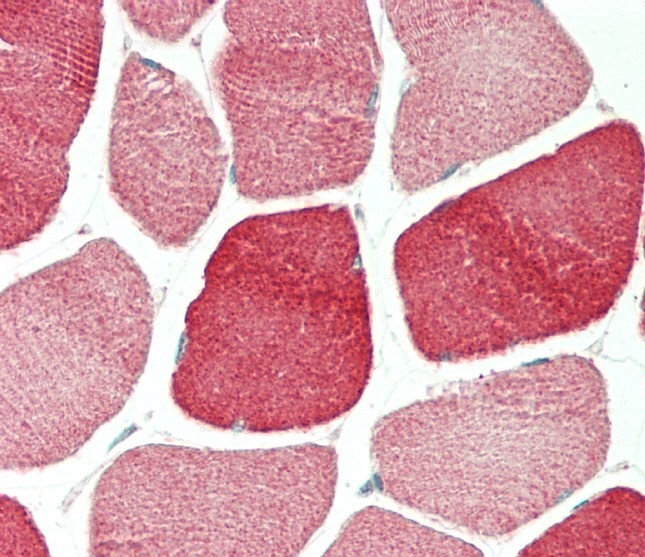
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Tropomyosin alpha-4 chain, TM30p1, Tropomyosin-4, TPM4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 7171 |
| WB Predicted band size | 28.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This TPM4 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 26-54 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human TPM4. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于TPM4(N-term)抗体的3篇模拟参考文献(注:内容为示例,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*TPM4 Expression in Colorectal Cancer and Its Role in Cell Migration*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用TPM4 (N-term)抗体通过免疫组化分析结直肠癌组织,发现TPM4在转移性肿瘤中高表达,并通过体外实验证实其通过调节细胞骨架重组促进癌细胞迁移。
2. **文献名称**:*Characterization of TPM4 Isoforms Using N-terminal Specific Antibodies*
**作者**:Lee C, et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,作者使用TPM4 (N-term)抗体鉴定了不同TPM4异构体在肌肉细胞中的分布,揭示了其在肌动蛋白纤维动态组装中的特异性功能。
3. **文献名称**:*TPM4 Interaction with Rho GTPase Signaling Pathways*
**作者**:Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)结合TPM4 (N-term)抗体,证实TPM4与RhoA蛋白存在直接相互作用,并调控细胞运动相关信号通路,为靶向癌症转移提供新视角。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“TPM4 antibody N-terminal”为关键词检索近年研究。
The TPM4 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of tropomyosin 4 (TPM4), a member of the tropomyosin family that regulates actin filament stability and dynamics in eukaryotic cells. Tropomyosins are coiled-coil proteins critical for cytoskeletal organization, cell motility, and intracellular trafficking. TPM4. encoded by the *TPM4* gene, is expressed in various tissues, including muscle, endothelial cells, and certain cancer cells, where it modulates actin-myosin interactions and cellular contractility. Its N-terminal domain plays a key role in binding actin filaments and influencing isoform-specific functions.
Antibodies against the N-terminal region of TPM4 are valuable tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions in physiological and pathological contexts. They are commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to investigate TPM4's role in processes such as cell migration, tumor metastasis, and cardiovascular function. Dysregulation of TPM4 has been linked to cancers, cardiomyopathies, and neurological disorders, making this antibody relevant for both basic research and clinical studies.
The specificity of TPM4 (N-term) antibodies is typically validated using knockout controls or peptide blocking assays to ensure accurate detection. Researchers utilize these antibodies to explore TPM4's involvement in signaling pathways, cytoskeletal remodeling, and disease mechanisms, contributing to a deeper understanding of its biological and therapeutic significance.
×