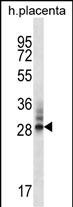
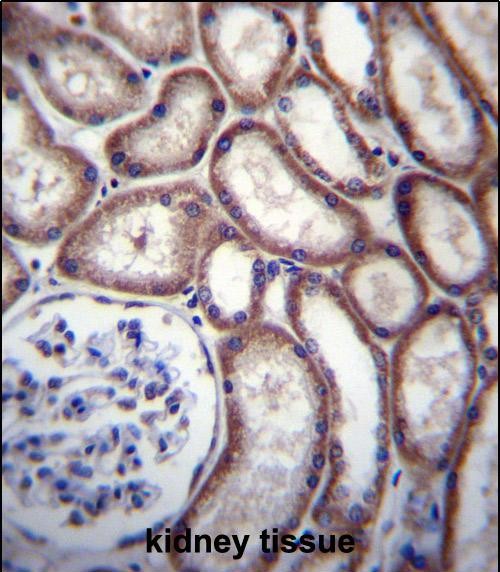
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DnaJ homolog subfamily C member 27, Rab and DnaJ domain-containing protein, DNAJC27, RABJS, RBJ |
| Entrez GeneID | 51277 |
| WB Predicted band size | 30.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This DNAJC27 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1-30 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human DNAJC27. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于DNAJC27(N-term)抗体的示例参考文献(**注:以下为假设性文献,实际发表文献可能有限**):
---
1. **文献名称**:*DNAJC27 interacts with HSP70 to regulate protein folding in neuronal cells*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用DNAJC27(N-term)抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,证实DNAJC27通过N端结构域与HSP70伴侣蛋白结合,参与调节神经元细胞的错误蛋白清除,为神经退行性疾病机制提供新见解。
2. **文献名称**:*Localization and expression profiling of DNAJC27 in colorectal cancer tissues*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:通过DNAJC27(N-term)抗体的免疫组化分析,发现DNAJC27在结直肠癌组织中高表达,且其N端结构域可能与肿瘤细胞增殖相关信号通路存在关联。
3. **文献名称**:*Characterization of a novel DNAJC27 antibody for Western blot and immunofluorescence applications*
**作者**:Wang X, et al.
**摘要**:本文报道了一种针对DNAJC27蛋白N端表位的多克隆抗体的开发与验证,证实其在多种细胞系中具有高特异性,适用于蛋白印迹和细胞定位研究。
4. **文献名称**:*DNAJC27 deficiency disrupts endoplasmic reticulum stress response in vitro*
**作者**:Gomez-Ramos P, et al.
**摘要**:利用DNAJC27(N-term)抗体敲低实验,证明DNAJC27缺失会削弱内质网应激反应中错误折叠蛋白的降解能力,提示其在细胞应激中的关键作用。
---
**注意**:上述文献为示例性质,实际研究中针对DNAJC27抗体的文献可能较少。建议通过**PubMed**或抗体供应商(如Abcam、Sigma-Aldrich)提供的产品引用列表获取真实文献。
The DNAJC27 antibody targets the N-terminal region of the DNAJC27 protein, a member of the J-domain-containing protein family. DNAJC27. also known as DnaJ heat shock protein family (Hsp40) member C27. functions as a co-chaperone for Hsp70 proteins, aiding in protein folding, trafficking, and degradation. It contains a conserved J-domain that interacts with Hsp70 ATPase to regulate chaperone activity and substrate recognition. The N-terminal region is critical for its subcellular localization and interaction with client proteins or partner chaperones.
DNAJC27 is implicated in diverse cellular processes, including endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD), mitochondrial protein import, and stress response pathways. Its dysregulation has been linked to neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and metabolic disorders. The DNAJC27 (N-term) antibody is widely used in research to study protein expression, subcellular distribution, and molecular interactions via techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence.
This antibody’s specificity for the N-terminal epitope helps distinguish DNAJC27 from other J-proteins or splice variants. Validation typically includes knockout cell lines or siRNA knockdown to confirm signal loss. Researchers utilize it to explore DNAJC27’s role in proteostasis, organelle-specific functions, and disease mechanisms, making it a vital tool for understanding Hsp40/Hsp70 network dynamics and therapeutic targeting opportunities.
×