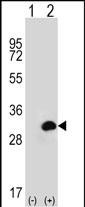
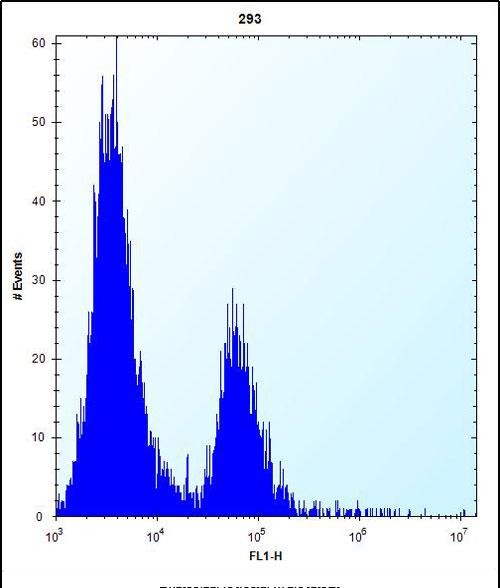
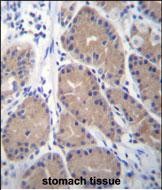
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Carbonic anhydrase 1, Carbonate dehydratase I, Carbonic anhydrase B, CAB, Carbonic anhydrase I, CA-I, CA1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 759 |
| WB Predicted band size | 28.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CA1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 60-90 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human CA1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
The CA1 (N-term) antibody is a polyclonal or monoclonal antibody specifically targeting the N-terminal region of human carbonic anhydrase 1 (CA1), a zinc-metalloenzyme belonging to the α-carbonic anhydrase family. CA1 catalyzes the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate and protons, playing critical roles in pH regulation, ion transport, and metabolic processes. It is predominantly expressed in erythrocytes and gastrointestinal tissues, with emerging associations in certain cancers and pathological conditions.
This antibody is commonly used in research applications such as Western blotting (WB), immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to detect CA1 expression in cell lysates, tissues, or biological fluids. Its specificity for the N-terminal epitope (e.g., residues 1-20) helps distinguish CA1 from other carbonic anhydrase isoforms (e.g., CA2. CA3) that share structural homology. Validation often includes knockdown experiments or CA1-deficient samples to confirm minimal cross-reactivity.
CA1 dysregulation has been implicated in diseases like ulcerative colitis, erythrocyte disorders, and tumors, making this antibody a tool for studying CA1's role in disease mechanisms or biomarker discovery. Commercial sources typically provide detailed validation data, including reactivity across human, mouse, or rat models. Researchers should optimize dilution ratios and protocols based on experimental systems to ensure reliable results.
×