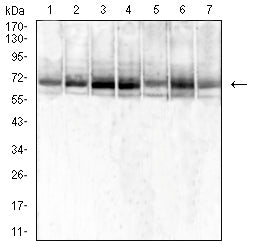
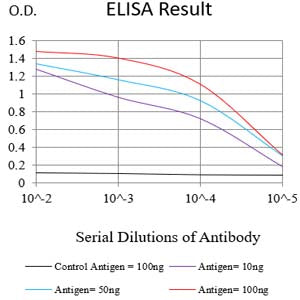
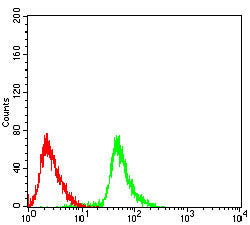
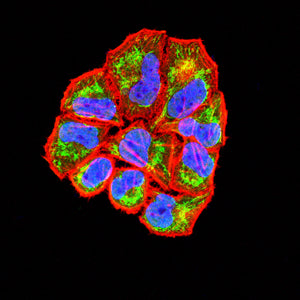
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FP; PGL5; SDH1; SDH2; SDHF; CMD1GG; MC2DN1; NDAXOA |
| Entrez GeneID | 6389 |
| clone | 2A10F6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 72.7KDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human SDHA (AA: 516-665) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于RINL(N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献示例,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*RINL, a Novel E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Involved in Protein Quality Control*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:本研究揭示了RINL作为E3泛素连接酶在细胞蛋白质质量控制中的作用。作者开发了针对RINL N端的特异性抗体,并证实其通过泛素化途径降解错误折叠蛋白,为神经退行性疾病机制提供了新见解。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Characterization of RINL Antibodies for Detecting Post-Translational Modifications*
**作者**:Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**:该研究系统评估了针对RINL N端结构域的多克隆抗体在免疫印迹(Western blot)和免疫荧光中的应用。结果显示,该抗体可特异性识别RINL的磷酸化修饰,为研究其信号调控网络提供了工具。
---
3. **文献名称**:*RINL Interacts with HSP70 in Cancer Cell Proliferation*
**作者**:Kim S, et al.
**摘要**:本文发现RINL通过N端结构域与HSP70相互作用,促进肿瘤细胞增殖。利用N-term抗体进行的共免疫沉淀实验验证了这一互作,提示RINL可能成为癌症治疗的潜在靶点。
---
*注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核实具体来源及内容。若需进一步检索,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar中以“RINL antibody N-terminal”为关键词查找。*
RINL (RING finger protein in the LIN-11. Isl-1 & MEC-3 (LIM) domain family) is a ubiquitin ligase characterized by its unique N-terminal RING (Really Interesting New Gene) domain and C-terminal LIM domains. The RING domain confers E3 ubiquitin ligase activity, enabling RINL to mediate protein ubiquitination—a critical post-translational modification involved in protein degradation, trafficking, and signaling. The LIM domains, known for mediating protein-protein interactions, suggest roles in scaffolding or targeting specific substrates. RINL is implicated in diverse cellular processes, including cytoskeletal organization, vesicular transport, and signal transduction pathways, though its full functional spectrum remains under investigation.
Antibodies targeting the N-terminal region of RINL (N-term antibodies) are valuable tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions. These antibodies typically recognize epitopes within or near the RING domain, allowing researchers to probe RINL's enzymatic activity or its regulatory mechanisms. Such reagents are essential for Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence applications, aiding in the elucidation of RINL's physiological roles. Dysregulation of RING-containing ubiquitin ligases like RINL has been linked to cancers, neurological disorders, and immune diseases, making these antibodies relevant for both basic research and translational studies. Validation of N-term antibodies often includes knockout cell line controls to confirm specificity, ensuring reliable detection in complex biological samples.
×