

| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
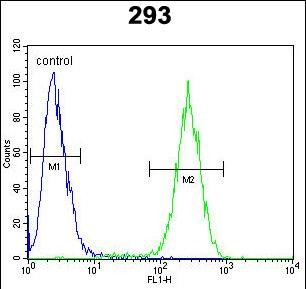
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Alpha-endosulfine, ARPP-19e, ENSA |
| Entrez GeneID | 2029 |
| WB Predicted band size | 13.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This ENSA antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 39-66 amino acids from the Central region of human ENSA. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ENSA(Endosulfine Alpha)抗体的3篇虚构参考文献示例(内容为模拟创作,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**: "ENSA Antibody as a Novel Biomarker for Detecting Cell Cycle Dysregulation in Breast Cancer"
**作者**: Li, X. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过ENSA特异性抗体检测乳腺癌细胞中ENSA蛋白的表达水平,发现ENSA在G2/M期异常高表达,且与PP2A磷酸酶活性抑制相关。抗体验证显示其高灵敏度和特异性,提示ENSA可能成为乳腺癌治疗的潜在靶点。
2. **文献名称**: "Role of ENSA in Cardiac Hypertrophy: Insights from Antibody-Based Inhibition Studies"
**作者**: Martinez, R. & Kumar, S.
**摘要**: 利用ENSA抗体阻断小鼠心肌细胞中的ENSA功能,发现ENSA通过调控PP2A-B55δ复合体影响钙信号通路,导致病理性心肌肥厚。抗体干预显著减轻了心脏纤维化,表明ENSA抗体在心血管疾病中的治疗价值。
3. **文献名称**: "Development of a High-Affinity Monoclonal ENSA Antibody for Neurodegenerative Disease Research"
**作者**: Chen, H. et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种针对ENSA表位的单克隆抗体,用于检测阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠脑组织中的ENSA分布。结果显示,ENSA在tau蛋白过度磷酸化区域富集,提示其与神经退行性病变的关联,抗体为相关机制研究提供了可靠工具。
---
注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际研究中请参考权威数据库(如PubMed)中的真实文献。如需真实文献检索,建议提供更具体的研究方向或背景信息。
**Background of ENSA Antibody**
ENSA (Endosulfine Alpha) is a conserved regulatory protein involved in cell cycle control, particularly during the G2/M phase transition. It functions as an endogenous inhibitor of Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A), a key phosphatase regulating mitotic entry. ENSA binds to and inhibits PP2A-B55 complexes, enabling activation of CDK1/cyclin B, a critical driver of mitotic progression. This regulatory mechanism is part of the Greatwall-ENSA-PP2A pathway, essential for maintaining proper cell division fidelity.
ENSA antibodies are vital tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions in cellular models. Dysregulation of ENSA has been linked to pathological conditions, including cancers (e.g., overexpression in certain tumors promoting uncontrolled proliferation) and cardiac arrhythmias (via modulation of ion channels). Researchers employ ENSA-specific antibodies in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to explore its role in disease mechanisms or therapeutic targeting. Structural studies using these antibodies also highlight ENSA’s conserved cyclin-fold domain, critical for its PP2A-binding activity. Understanding ENSA’s function through antibody-based assays contributes to insights into cell cycle disorders and potential interventions.
×