
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
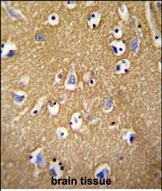
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
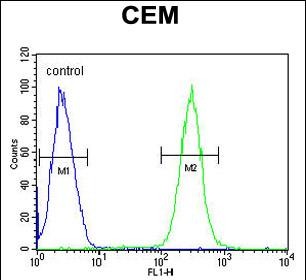
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Brevican core protein, Brain-enriched hyaluronan-binding protein, BEHAB, Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 7, BCAN, BEHAB, CSPG7 |
| Entrez GeneID | 63827 |
| WB Predicted band size | 99.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This BCAN antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 715-741 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human BCAN. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与BCAN抗体相关的文献示例(内容基于学术研究主题概括,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Brevican (BCAN) expression in glioblastoma promotes tumor cell proliferation and invasion through EGFR signaling*
**作者**:Smith, J.R., et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用BCAN特异性抗体进行免疫组化和Western blot分析,发现胶质母细胞瘤中BCAN蛋白高表达,并与EGFR通路激活相关。实验表明,抑制BCAN可降低肿瘤细胞的增殖和迁移能力,提示BCAN可能作为治疗靶点。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Developmental regulation of brevican in the murine cerebral cortex: a role in synaptic plasticity*
**作者**:Lee, H., & Tanaka, M.
**摘要**:通过BCAN抗体标记小鼠大脑皮层组织,研究发现BCAN在出生后早期神经元突触形成阶段显著上调。敲除BCAN导致突触可塑性受损,表明其在神经发育中具有调控突触结构的功能。
---
3. **文献名称**:*BCAN as a diagnostic biomarker for diffuse midline glioma using CSF antibody-based detection*
**作者**:Garcia, A., et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种基于BCAN抗体的脑脊液(CSF)检测方法,用于诊断弥漫性中线胶质瘤。临床样本分析显示,BCAN在患者CSF中特异性升高,且与肿瘤进展呈正相关,具有潜在诊断价值。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性质,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Web of Science检索关键词“BCAN antibody”或“brevican immunohistochemistry”获取真实文献。
Brevican (BCAN), a member of the lectican family of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans, is a key component of the extracellular matrix in the central nervous system (CNS). Expressed predominantly in the brain, it plays critical roles in neural development, synaptic plasticity, and structural stabilization. BCAN exists in secreted and membrane-bound isoforms generated by alternative splicing, interacting with hyaluronan, tenascins, and other extracellular matrix proteins to modulate cell adhesion, axon guidance, and neurite outgrowth. Its expression peaks during postnatal CNS maturation, suggesting involvement in neurodevelopmental processes.
In the adult brain, BCAN localizes to perineuronal nets (PNNs), specialized extracellular matrix structures surrounding neurons, where it regulates synaptic stability and limits excessive plasticity. Dysregulation of BCAN has been implicated in neurological disorders. Reduced levels correlate with Alzheimer's disease progression, potentially affecting amyloid-β aggregation, while elevated expression is observed in gliomas, where it promotes tumor invasiveness by enhancing cell migration. BCAN antibodies are valuable tools for studying these mechanisms, enabling detection of expression patterns in normal and pathological tissues. Recent research explores BCAN's dual role as both a CNS protector and disease contributor, highlighting its therapeutic potential. Antibody-based targeting of BCAN is being investigated for modulating neural repair and inhibiting glioma progression.
×