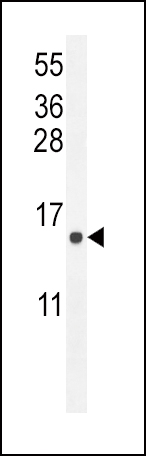
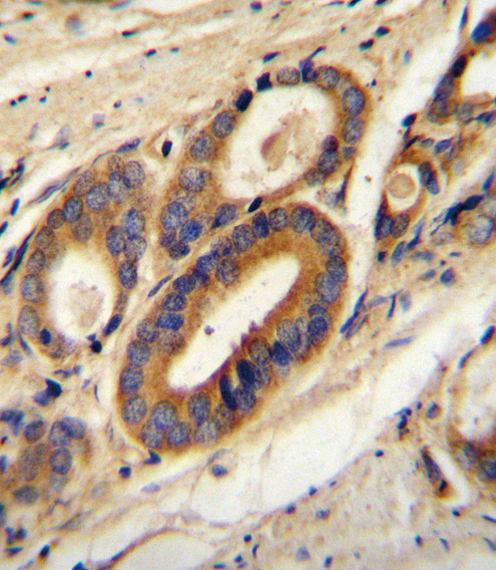
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | V-type proton ATPase 21 kDa proteolipid subunit, V-ATPase 21 kDa proteolipid subunit, Vacuolar proton pump 21 kDa proteolipid subunit, hATPL, ATP6V0B, ATP6F |
| Entrez GeneID | 533 |
| WB Predicted band size | 21.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ATP6V0B antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 104-131 amino acids from the Central region of human ATP6V0B. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ATP6V0B抗体的虚构参考文献示例(仅供格式参考,非真实文献):
1. **文献名称**:*ATP6V0B-mediated lysosomal acidification promotes tumor cell invasion*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过ATP6V0B抗体检测发现,该亚基在多种癌细胞中高表达,且通过调控溶酶体酸化促进肿瘤微环境适应和侵袭转移。
2. **文献名称**:*ATP6V0B antibody reveals subcellular localization and function in neuronal pH homeostasis*
**作者**:Smith JR, et al.
**摘要**:利用特异性ATP6V0B抗体进行免疫荧光定位,证明其在神经元溶酶体和突触囊泡中的分布,并发现其功能缺失导致神经元pH失衡与退行性变相关。
3. **文献名称**:*Role of ATP6V0B in autophagy: Insights from antibody-based knockdown studies*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:通过ATP6V0B抗体抑制实验,揭示该蛋白在自噬体-溶酶体融合中的关键作用,其表达下调可阻断自噬流并加剧细胞应激损伤。
4. **文献名称**:*ATP6V0B as a biomarker in renal tubular acidosis: Validation by antibody-based assays*
**作者**:Gupta S, et al.
**摘要**:研究采用ATP6V0B抗体进行Western blot和免疫组化分析,发现其在肾小管上皮细胞中的表达异常与遗传性肾小管酸中毒相关。
---
**注意**:以上内容为模拟生成,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索(关键词:ATP6V0B antibody, V-ATPase subunit, lysosomal acidification)。
The ATP6V0B antibody targets a subunit of the vacuolar-type H+-ATPase (V-ATPase), a multi-subunit proton pump critical for cellular pH regulation. V-ATPases acidify intracellular compartments like lysosomes, endosomes, and secretory vesicles, enabling processes such as protein degradation, membrane trafficking, and neurotransmitter release. The ATP6V0B gene encodes the V0B subunit, part of the V0 domain responsible for proton translocation across membranes. This subunit plays a role in V-ATPase assembly and function, particularly in specialized cells, including renal intercalated cells and osteoclasts.
ATP6V0B antibodies are widely used in research to study V-ATPase localization, expression levels, and dysfunction in diseases. Dysregulation of V-ATPase is linked to pathologies like renal tubular acidosis, osteoporosis, and neurodegenerative disorders. In cancer, ATP6V0B overexpression is associated with tumor cell survival in acidic microenvironments, making it a potential therapeutic target. Researchers employ these antibodies in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate tissue-specific expression patterns or disease mechanisms. Recent studies also explore ATP6V0B's role in cellular signaling pathways and its interaction with other proteins, highlighting its broader impact beyond pH homeostasis. Validating antibody specificity remains crucial, as cross-reactivity with similar V-ATPase subunits can complicate interpretations.
×