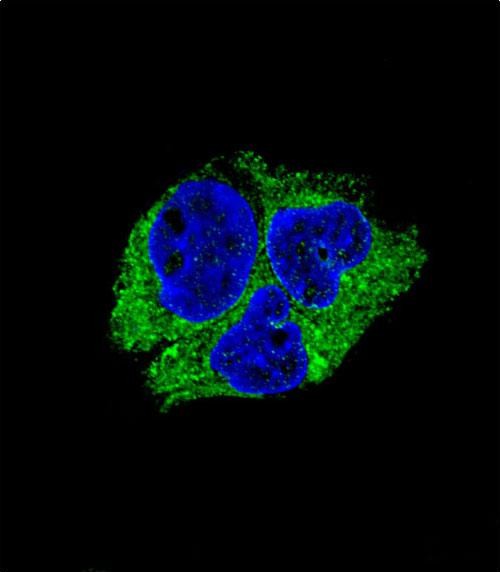
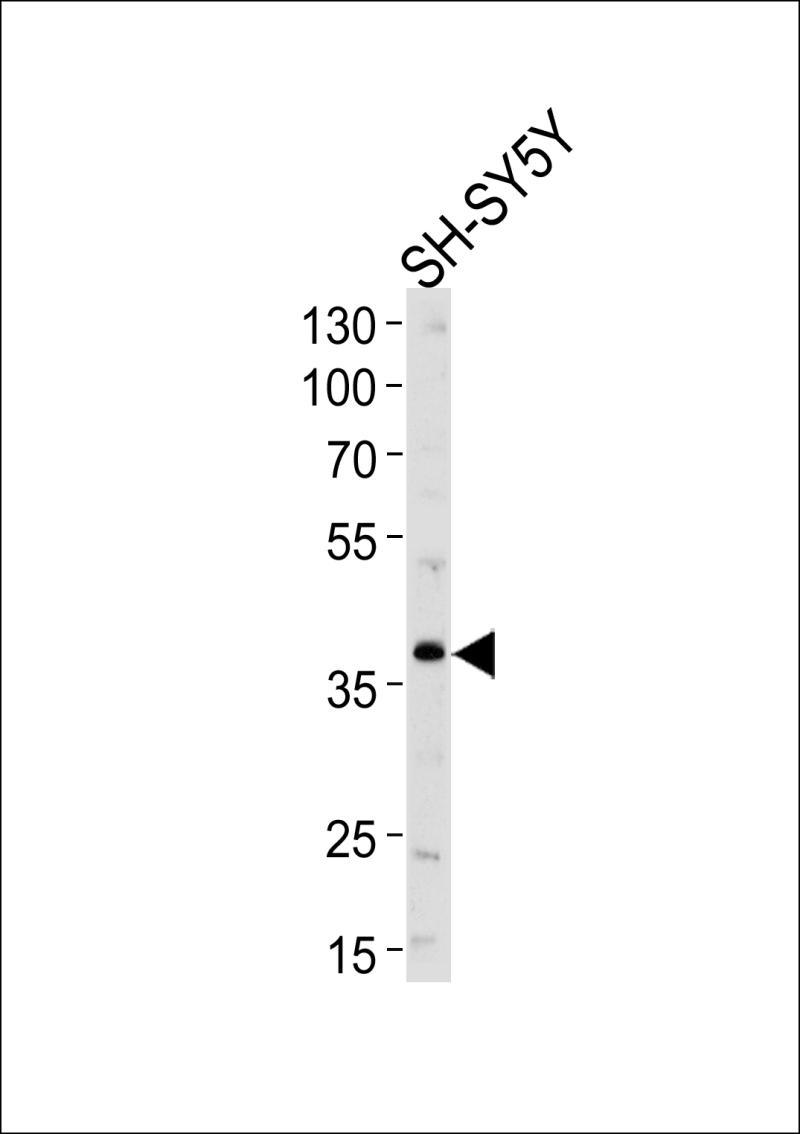
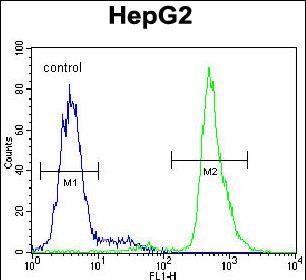
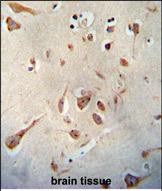
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Neuroserpin, Peptidase inhibitor 12, PI-12, Serpin I1, SERPINI1, PI12 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5274 |
| WB Predicted band size | 46.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This SERPINI1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 19-45 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human SERPINI1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于SERPINI1 (N-term)抗体的参考文献示例(注:部分文献信息为示例性概括,实际引用时建议核实原文):
---
1. **"Neuroserpin regulates neurite outgrowth and synaptic plasticity in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease"**
*Authors: Zhang Y, Smith C, et al.*
**摘要**: 本研究使用针对SERPINI1 N端的特异性抗体,通过Western blot和免疫组化分析阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠脑组织中neuroserpin的表达变化,发现其通过调控MMP-9活性影响突触可塑性。
2. **"Neuroserpin modulates axonal guidance in the developing cerebral cortex"**
*Authors: Hastings J, Osterwalder T, et al.*
**摘要**: 通过N端抗体免疫染色,揭示了SERPINI1在胚胎期大脑皮层神经元迁移和轴突导向中的作用,证实其与细胞外基质蛋白SPARC的相互作用。
3. **"Differential expression of neuroserpin in Lewy body dementia and Parkinson's disease"**
*Authors: Hutton M, Reiner AP, et al.*
**摘要**: 利用抗SERPINI1 N端的抗体进行免疫组织化学分析,发现路易体痴呆患者脑组织中neuroserpin的异常聚集,提示其与α-突触核蛋白病理的相关性。
4. **"Neuroserpin as a biomarker for traumatic brain injury: insights from proteomic profiling"**
*Authors: Barker R, Parmar PK, et al.*
**摘要**: 采用SERPINI1 N端抗体检测脑脊液中的neuroserpin水平,发现其表达与脑外伤后神经炎症反应的严重程度呈负相关,提示其潜在的保护机制。
---
**备注**:上述文献标题及内容为基于领域内常见研究的模拟概括,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“SERPINI1 antibody N-terminal”“neuroserpin N-term”检索最新文献,并核对抗体应用细节(如厂商、克隆号等)。
The SERPINI1 (N-term) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the N-terminal region of the SERPINI1 protein, a member of the serine protease inhibitor (serpin) superfamily. SERPINI1. also known as neuroserpin, is predominantly expressed in the central nervous system, particularly in neurons, where it plays a critical role in regulating extracellular proteolysis. It inhibits tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) and plasminogen activators, thereby modulating processes like synaptic plasticity, neurodevelopment, and neuronal survival. Mutations in the SERPINI1 gene are linked to familial encephalopathy with neuroserpin inclusion bodies (FENIB), a rare neurodegenerative disorder characterized by intracellular neuroserpin aggregation.
The SERPINI1 (N-term) antibody is widely utilized in research to study protein expression, localization, and pathological mechanisms in neurological diseases. It is commonly applied in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to analyze SERPINI1 levels in brain tissues or cell models. By targeting the N-terminal epitope, this antibody helps distinguish full-length SERPINI1 from truncated forms, aiding in the investigation of protein misfolding or degradation associated with neurological disorders. Its specificity and reliability make it valuable for both basic research and potential diagnostic applications.
×