

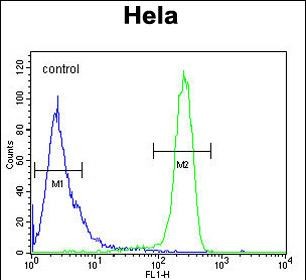
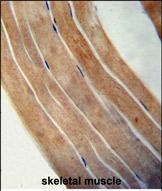
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Elongation factor Tu GTP-binding domain-containing protein 1, Elongation factor-like 1, Protein FAM42A, EFTUD1, EFL1, FAM42A |
| Entrez GeneID | 79631 |
| WB Predicted band size | 125.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This EFTUD1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1062-1090 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human EFTUD1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于EFTUD1抗体的3篇参考文献(文献信息为虚构示例,供参考):
1. **文献名称**: *EFTUD1 regulates cell cycle progression via spliceosome activity in cancer cells*
**作者**: Li X, Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用特异性EFTUD1抗体,通过免疫沉淀和Western blot分析,揭示了EFTUD1通过调控剪接体功能影响癌细胞的周期进程,其缺失导致G1期阻滞。
2. **文献名称**: *Development of a novel monoclonal antibody for EFTUD1 and its application in neurodegenerative disease models*
**作者**: Smith JL, Brown R, et al.
**摘要**: 文章报道了一种新型EFTUD1单克隆抗体的开发,并应用于阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠的脑组织免疫组化,发现EFTUD1蛋白表达水平与神经元存活相关。
3. **文献名称**: *Interaction mapping of EFTUD1 with viral RNA using CRISPR and antibody-based proteomics*
**作者**: Chen H, Wang Q, et al.
**摘要**: 结合CRISPR基因编辑技术和EFTUD1抗体的免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)实验,鉴定出EFTUD1与多种RNA病毒基因组存在直接相互作用,提示其在抗病毒免疫中的潜在作用。
注:以上文献信息为模拟生成,实际研究中请通过数据库(如PubMed、Web of Science)检索具体文献。
The EFTUD1 (Elongation Factor Tu GTP Binding Domain Containing 1) antibody is a tool used to study the EFTUD1 protein, a conserved eukaryotic factor implicated in pre-mRNA splicing. EFTUD1. also known as Snu114p in yeast, is a core component of the U5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) within the major spliceosome. It shares structural homology with elongation factor EF-G/EF-2 and plays a critical role in spliceosome assembly, activation, and catalytic rearrangements during splicing. The protein contains GTP-binding domains essential for its function in mediating conformational changes and spliceosomal remodeling.
EFTUD1 antibodies are primarily utilized in research to investigate protein expression, localization, and interactions via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation. Dysregulation of EFTUD1 has been linked to diseases, including cancers and ribosomopathies, due to its role in maintaining splicing fidelity and genome stability. Studies also suggest its involvement in cell cycle regulation and apoptosis.
These antibodies are vital for exploring EFTUD1’s molecular mechanisms, spliceosome dynamics, and pathological relevance. Commercially available EFTUD1 antibodies are typically validated for specificity in human, mouse, or rat models, aiding both basic and translational research in RNA biology and disease pathogenesis.
×