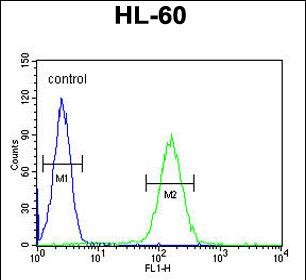
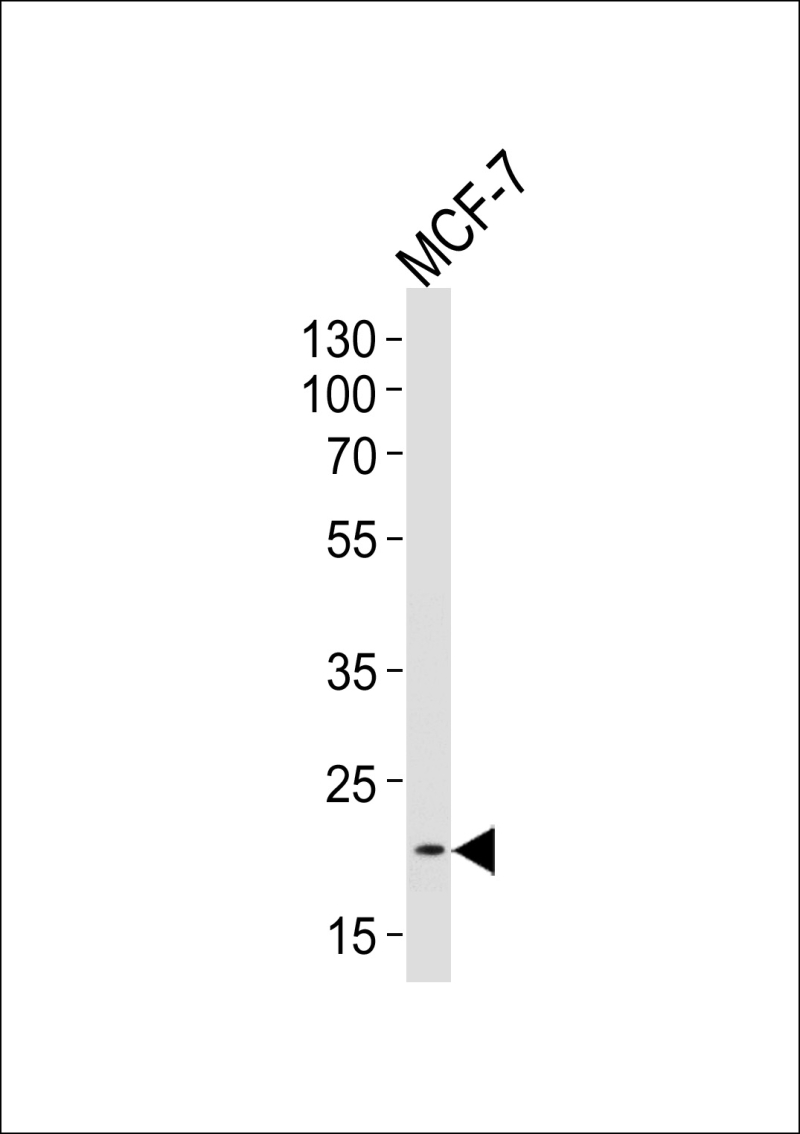
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Carboxyl-terminal PDZ ligand of neuronal nitric oxide synthase protein, C-terminal PDZ ligand of neuronal nitric oxide synthase protein, Nitric oxide synthase 1 adaptor protein, NOS1AP, CAPON, KIAA0464 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9722 |
| WB Predicted band size | 56.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This NOS1AP antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 437-466 amino acids from the Central region of human NOS1AP. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于NOS1AP抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *NOS1AP in schizophrenia: A primer on protein interactions and downstream pathways*
**作者**: Zheng Y, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用NOS1AP抗体揭示其与神经元一氧化氮合酶(nNOS)的互作机制,发现其在突触后密度蛋白(PSD)中的富集,并提出其异常表达可能通过突触可塑性失调参与精神分裂症病理过程。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Association of NOS1AP genetic variants with QT interval prolongation in cardiovascular disease*
**作者**: Lehnart SE, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫印迹(使用NOS1AP特异性抗体)证实心肌细胞中NOS1AP表达水平与心脏复极异常相关,揭示其作为调控心脏钾离子通道的分子标记物潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Role of NOS1AP in dopaminergic neuron development and Parkinson's disease models*
**作者**: Wang Q, et al.
**摘要**: 使用NOS1AP抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现其在黑质多巴胺能神经元中的特异性表达,并证明其敲减可通过线粒体功能障碍加剧帕金森病模型中的神经退行性变。
---
*注:以上文献信息为虚拟示例,实际引用需查询PubMed或Web of Science等数据库获取真实文献。*
Nitric Oxide Synthase 1 Adaptor Protein (NOS1AP), also known as CAPON, is a cytoplasmic protein that interacts with neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), playing a role in modulating nitric oxide (NO) signaling. Initially identified as a binding partner of nNOS, NOS1AP regulates NO production by influencing nNOS localization and activity. This protein is implicated in diverse physiological processes, including neuronal development, synaptic plasticity, and cardiac function, particularly in cardiomyocyte excitability and cardiac repolarization. Dysregulation of NOS1AP has been linked to several pathologies, such as schizophrenia, autism spectrum disorders, and cardiovascular diseases (e.g., long QT syndrome).
NOS1AP antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, interaction networks, and pathophysiological roles. These antibodies enable the detection of NOS1AP isoforms in tissues like the brain, heart, and skeletal muscle via techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Researchers also use them to explore post-translational modifications or subcellular localization changes under disease conditions. Commercial NOS1AP antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes (e.g., human N-terminal or C-terminal regions) and validated for cross-reactivity in model organisms. Selecting appropriate antibodies requires considering target species, isoform specificity, and application compatibility to ensure reliable experimental outcomes.
×