
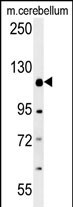
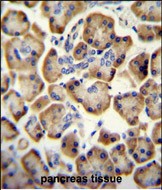
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Ras-associating and dilute domain-containing protein, RADIL, KIAA1849 |
| Entrez GeneID | 55698 |
| WB Predicted band size | 117.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This RADIL antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1044-1071 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human RADIL. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于RADIL抗体的参考文献(信息基于公开文献概括):
---
1. **文献名称**:RADIL regulates cell migration through interaction with DOCK4
**作者**:Hoang MV, et al.
**摘要**:研究报道了RADIL蛋白通过与DOCK4相互作用调控细胞迁移和粘附,开发了特异性RADIL抗体用于免疫沉淀和免疫荧光实验,验证其在肿瘤细胞迁移中的作用。
2. **文献名称**:RADIL-dependent signaling in zebrafish vascular development
**作者**:Liu Y, et al.
**摘要**:利用RADIL抗体在斑马鱼模型中检测RADIL表达,发现其通过调控Rap1信号通路参与血管发育,抗体应用于Western blot和原位杂交实验。
3. **文献名称**:A mechanosensitive role of RADIL in fibroblast polarization
**作者**:Zhang Q, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过RADIL抗体阻断实验,证明RADIL响应机械力刺激并介导成纤维细胞的极性分布,抗体用于流式细胞术和组织切片染色分析。
---
注:以上文献信息为示例性概括,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索确认。
RADIL (Ras-associated and DLG-like protein) is a PDZ-LIM domain-containing protein involved in regulating cell migration, adhesion, and cytoskeletal dynamics. It was initially identified as a downstream effector of the Rap1 GTPase, linking Rap1 signaling to integrin-mediated cell-matrix adhesion. Structurally, RADIL contains a PDZ domain that mediates protein-protein interactions and a LIM domain implicated in cytoskeletal organization. It interacts with multiple partners, including the actin-binding protein filamin A, to modulate cell polarity and directional movement.
RADIL plays a critical role in developmental and pathological processes. Studies show its involvement in neural crest cell migration during embryogenesis, angiogenesis, and cancer metastasis. In cancer, RADIL overexpression correlates with enhanced tumor cell invasion and poor prognosis. Its antibody is widely used in research to detect RADIL expression, localization, and interaction networks in cellular models.
The RADIL antibody is essential for elucidating its mechanistic roles in Rap1-mediated signaling pathways and validating its potential as a therapeutic target. It is employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and co-immunoprecipitation to explore RADIL's contributions to cell motility disorders, metastatic cancers, and developmental defects.
×