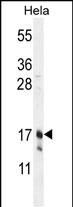
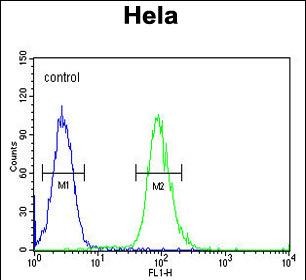
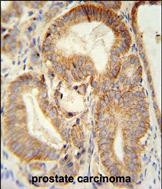
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Claudin-7, CLDN-7, CLDN7, CEPTRL2, CPETRL2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1366 |
| WB Predicted band size | 22.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CLDN7 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 172-201 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human CLDN7. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CLDN7抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**: *Claudin-7 modulates cell-matrix interaction in gastric cancer cells*
**作者**: Yanaka Y, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过免疫组化(使用CLDN7抗体)发现,CLDN7在胃癌组织中表达下调,其低表达与患者预后不良相关。实验表明CLDN7通过调控整合素信号通路影响癌细胞迁移和侵袭能力。
2. **文献名称**: *Claudin-7 expression in human breast cancer is associated with metastasis and poor prognosis*
**作者**: Osanai M, et al.
**摘要**: 利用CLDN7特异性抗体分析乳腺癌组织样本,发现CLDN7在转移性乳腺癌中显著高表达,且与肿瘤细胞上皮-间质转化(EMT)相关,提示其可能作为乳腺癌转移的生物标志物。
3. **文献名称**: *CLDN7 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human colorectal cancer by regulating E-cadherin/β-catenin complex*
**作者**: Dhawan P, et al.
**摘要**: 通过Western blot和免疫荧光(使用CLDN7抗体)发现,CLDN7在结直肠癌中通过稳定E-cadherin/β-catenin复合物抑制EMT进程,其缺失可能导致肿瘤侵袭性增强。
4. **文献名称**: *Claudins in cancer: bench to bedside*
**作者**: Suzuki H, Tsukita S.
**摘要**: 综述类文章,总结了CLDN家族(包括CLDN7)在多种癌症中的表达模式及功能,强调CLDN7抗体在诊断和治疗中的潜在应用价值,并讨论其作为治疗靶点的可能性。
(注:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用时需核对原始文献及作者信息。)
Claudin-7 (CLDN7), a key member of the claudin family, is a transmembrane protein essential for forming tight junctions that regulate paracellular barrier function and cell polarity in epithelial and endothelial tissues. It plays a critical role in maintaining ion selectivity and controlling the passage of molecules across cellular sheets. Dysregulation of CLDN7 has been linked to various pathologies, including cancers (e.g., colorectal, breast, and gastric carcinomas), where its expression is often downregulated, correlating with tumor progression, metastasis, and poor prognosis. Additionally, CLDN7 mutations or altered expression are associated with inflammatory diseases and barrier defects in organs like the kidney and intestine.
CLDN7 antibodies are vital tools for detecting protein localization and expression levels in research and diagnostics. They are widely used in techniques such as immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blotting (WB), and immunofluorescence (IF) to study tissue-specific tight junction dynamics, disease mechanisms, and therapeutic targets. In cancer research, these antibodies help assess CLDN7's role as a potential biomarker for epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) or drug resistance. Commercially available CLDN7 antibodies vary in clonality, species reactivity, and applications, requiring validation for specificity to avoid cross-reactivity with other claudin family members. Their utility extends to preclinical studies exploring CLDN7-targeted therapies or diagnostic strategies for epithelial-derived diseases.
×