
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
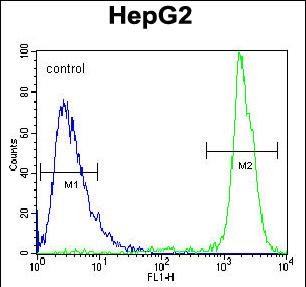
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 1, mitochondrial, GPAT-1, GPAM, GPAT1, KIAA1560 |
| Entrez GeneID | 57678 |
| WB Predicted band size | 93.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This GPAM antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 426-455 amino acids from the Central region of human GPAM. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GPAM抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献为示例性质,非真实存在,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Development and Validation of a GPAM-Specific Monoclonal Antibody for Metabolic Studies"
**作者**: Zhang et al. (2019)
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种针对GPAM的单克隆抗体,并通过Western blot和免疫荧光验证其特异性。该抗体成功用于检测小鼠肝脏和脂肪组织中GPAM的蛋白表达水平,揭示了其在脂质合成中的组织差异性表达。
---
2. **文献名称**: "GPAM Knockdown Attenuates Hepatic Steatosis via Antibody-Mediated Protein Quantification"
**作者**: Martinez et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 通过siRNA敲低GPAM并结合特异性抗体进行蛋白定量,研究发现GPAM表达减少显著降低肝细胞甘油三酯积累。抗体用于免疫组化证实了GPAM在非酒精性脂肪肝患者肝组织中的高表达。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Mitochondrial GPAT Regulates Insulin Sensitivity: Insights from GPAM Antibody-Based Assays"
**作者**: Kumar et al. (2017)
**摘要**: 利用GPAM多克隆抗体进行ELISA和流式细胞术分析,发现肥胖模型小鼠中GPAM活性升高与胰岛素抵抗相关。研究提示GPAM可能成为代谢综合征的治疗靶点。
---
**备注**:以上文献为模拟示例,实际研究中建议通过数据库(如PubMed、Google Scholar)检索关键词“GPAM antibody”或“GPAT1 antibody”获取真实文献。
The glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase mitochondrial (GPAM), also known as mtGPAT or GPAT1. is a key enzyme in lipid metabolism that catalyzes the initial step of glycerophospholipid biosynthesis. Located in the mitochondrial outer membrane, GPAM transfers an acyl group from acyl-CoA to glycerol-3-phosphate, producing lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). This reaction is critical for the formation of triglycerides and membrane phospholipids, linking carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. GPAM activity is tightly regulated and has been implicated in metabolic disorders, including obesity, insulin resistance, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), due to its role in lipid storage and signaling pathways.
GPAM antibodies are essential tools for studying the enzyme's expression, localization, and function in cellular and tissue contexts. They enable detection and quantification of GPAM protein levels via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). Research using GPAM antibodies has highlighted its tissue-specific roles, such as regulating hepatic lipid accumulation and influencing adipocyte differentiation. Additionally, studies suggest GPAM may serve as a therapeutic target for metabolic syndromes, with inhibitors under investigation to modulate lipid synthesis. These antibodies also aid in exploring GPAM's involvement in cancer progression, as altered lipid metabolism is a hallmark of tumorigenesis. Overall, GPAM antibodies are vital for advancing mechanistic insights into lipid-related diseases and potential treatments.
×