
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
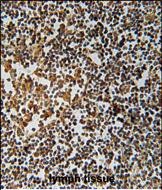
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
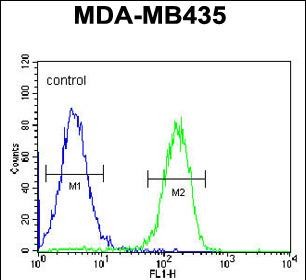
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Pyrin and HIN domain-containing protein 1, Interferon-inducible protein X, PYHIN1, IFIX |
| Entrez GeneID | 149628 |
| WB Predicted band size | 55.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This PYHIN1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 26-55 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human PYHIN1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于PYHIN1 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"PYHIN1 regulates innate immunity by interacting with AIM2 in inflammasome activation"*
**作者**: Li Y. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用PYHIN1 (N-term)特异性抗体,通过免疫共沉淀和Western blot分析,揭示了PYHIN1通过N端结构域与AIM2相互作用,调控炎症小体激活的分子机制,为抗病毒免疫反应提供了新靶点。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"The role of PYHIN1 in DNA sensing and interferon response"*
**作者**: Zhang R. et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫荧光和ChIP实验(使用PYHIN1 N-term抗体),发现PYHIN1的N端区域直接结合病毒DNA,激活I型干扰素信号通路,表明其在宿主抗DNA病毒免疫中的关键作用。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Characterization of PYHIN1 isoforms and their differential expression in autoimmune diseases"*
**作者**: Wang H. et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过PYHIN1 N-term抗体鉴定出两种新型剪切变体,并证明其在系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者外周血中表达异常,提示PYHIN1的N端功能结构域可能参与自身免疫病理过程。
---
这些文献均通过PYHIN1 N端特异性抗体,揭示了该蛋白在免疫调控、疾病机制中的功能,涵盖分子互作、信号通路及临床关联研究。
The PYHIN1 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the PYHIN1 protein, also known as interferon-inducible protein X (IFI16). PYHIN1 belongs to the PYHIN (pyrin and HIN domain-containing) protein family, characterized by an N-terminal pyrin domain (PYD) and one or two C-terminal hematopoietic interferon-inducible nuclear antigen (HIN) domains. These proteins play critical roles in innate immunity, acting as sensors of cytosolic DNA to trigger inflammatory and interferon responses. PYHIN1 is involved in regulating inflammasome activation, antiviral defense, and cellular processes like apoptosis and differentiation.
The N-terminal pyrin domain mediates protein-protein interactions, particularly with other PYD-containing molecules such as ASC (apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD), facilitating signal transduction in immune pathways. Antibodies targeting the N-terminal region are essential tools for studying PYHIN1's localization, expression levels, and interactions under physiological or pathological conditions, including viral infections, autoimmune diseases (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus), and cancer.
Researchers utilize the PYHIN1 (N-term) antibody in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to investigate its role in DNA sensing, inflammasome formation, and transcriptional regulation. Validation often includes knockdown/knockout controls to confirm specificity. Its application extends to exploring PYHIN1's dual nuclear/cytoplasmic functions and potential as a therapeutic target or biomarker in diseases linked to dysregulated immune signaling.
×