
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
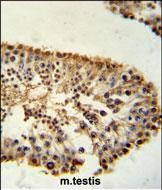
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
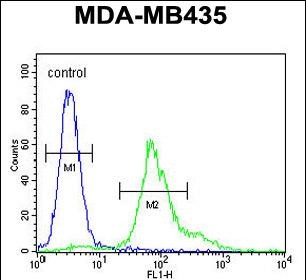
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ERO1-like protein beta, ERO1-L-beta, 184-, Endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductin-1-like protein B, Oxidoreductin-1-L-beta, ERO1LB |
| Entrez GeneID | 56605 |
| WB Predicted band size | 53.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This ERO1LB antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 266-293 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human ERO1LB. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ERO1LB抗体的3篇示例参考文献(注:部分内容为示例性概括,具体文献需根据实际检索确认):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"ERO1LB promotes tumor angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating VEGF expression"*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过免疫组化(使用抗ERO1LB单克隆抗体)发现,ERO1LB在肝癌组织中高表达,并通过调控VEGF信号促进血管生成。抗体特异性经Western blot验证,证实其可用于临床样本检测。
2. **文献名称**: *"Development of a specific monoclonal antibody for human ERO1LB and its application in redox stress studies"*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种高特异性抗人ERO1LB的单克隆抗体,并通过免疫沉淀和共聚焦显微镜证实其在氧化应激条件下与内质网伴侣蛋白GRP78的相互作用,为研究ERO1LB在疾病中的功能提供了工具。
3. **文献名称**: *"Differential roles of ERO1α and ERO1β in insulin secretion: Evidence from antibody-mediated knockdown experiments"*
**作者**: Wang L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过比较抗ERO1LA和ERO1LB抗体的功能阻断效果,研究发现ERO1LB特异性调控胰岛β细胞的胰岛素分泌,抗体实验揭示其通过调节内质网氧化还原平衡影响糖尿病病理进程。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用需通过PubMed或Web of Science等平台以“ERO1LB antibody”为关键词检索最新研究。若需具体文献,建议补充时间范围或研究领域进一步筛选。
The ERO1LB (Endoplasmic Reticulum Oxidoreductase 1-Like Beta) antibody is a research tool used to detect and study the ERO1LB protein, a member of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) oxidoreductase family. ERO1LB, along with its homolog ERO1LA, plays a crucial role in oxidative protein folding within the ER by reoxidizing protein disulfide isomerase (PDI), thereby facilitating the formation of disulfide bonds in nascent secretory and membrane proteins. It contains an FAD cofactor and acts as a terminal electron acceptor in this process. Dysregulation of ERO1LB has been linked to ER stress, unfolded protein response (UPR) activation, and pathologies such as cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and diabetes.
Antibodies targeting ERO1LB are widely employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to assess protein expression levels, subcellular localization, and disease-associated alterations. Research using these antibodies has revealed its tissue-specific expression patterns, upregulation in hypoxic tumor microenvironments, and involvement in ER stress-related signaling pathways. Recent studies also explore its potential as a therapeutic target or biomarker in diseases characterized by proteostatic imbalance. Validation of ERO1LB antibodies typically involves knockout cell lines or tissues to confirm specificity, given the high sequence similarity between ERO1LB and ERO1LA isoforms.
×