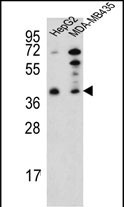
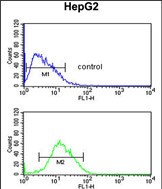
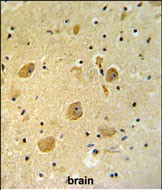
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Mono [ADP-ribose] polymerase PARP16, ADP-ribosyltransferase diphtheria toxin-like 15, Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 16, PARP-16, PAR16 |
| Entrez GeneID | 54956 |
| WB Predicted band size | 36.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This PARP16 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 215-244 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human PARP16. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于PARP16抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概述:
---
1. **"PARP16 is a tail-anchored endoplasmic reticulum protein required for GRP78 chaperone activity"**
*Authors: Jwa M, Chang P*
**摘要**:该研究通过开发特异性PARP16抗体,证实了PARP16作为内质网定位的酶,调控分子伴侣GRP78的活性。Western blot和免疫荧光显示,PARP16缺失会削弱内质网应激反应,抗体验证了其在未折叠蛋白反应中的关键作用。
---
2. **"PARP16-mediated ADP-ribosylation of a vesicle transport protein controls dengue virus replication"**
*Authors: Leung AKL, et al.*
**摘要**:研究利用PARP16抗体进行免疫沉淀和共定位分析,发现PARP16通过ADP-核糖基化修饰囊泡运输蛋白,促进登革病毒复制。抗体特异性在敲除细胞模型中得到验证,揭示了其抗病毒药物开发的潜力。
---
3. **"PARP16/ARTD15 is a novel endoplasmic reticulum-associated transferase and regulates the secretory pathway"**
*Authors: Di Paola S, et al.*
**摘要**:该文献报道了PARP16抗体在蛋白质分泌研究中的应用,通过免疫组化与功能实验,证明PARP16通过修饰内质网相关蛋白调控分泌途径,抗体特异性在基因敲除实验中得到确认。
---
**备注**:若需更多文献,可进一步检索近年研究(如肿瘤或代谢疾病领域),部分研究可能侧重功能机制,但通常包含抗体验证环节。
PARP16 (Poly-ADP-ribose polymerase 16), also known as ARTD6. is a member of the ADP-ribosyltransferase family involved in post-translational protein modification through mono- or poly-ADP-ribosylation. Unlike other PARP family members, PARP16 is anchored to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane and plays a role in ER stress response, cellular homeostasis, and apoptosis. It interacts with key stress sensors like PERK and IRE1α, modulating the unfolded protein response (UPR) to regulate cell survival under stress conditions. PARP16’s enzymatic activity has been linked to cancer progression, metabolic disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases, making it a potential therapeutic target.
PARP16 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in cellular and disease contexts. These antibodies enable detection via techniques such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry, aiding in investigations of PARP16’s role in ER stress signaling, autophagy, and cancer cell adaptation. Specific antibodies targeting distinct domains (e.g., catalytic or transmembrane regions) help dissect structure-function relationships. Validated antibodies are critical for ensuring specificity, particularly given structural similarities among PARP family proteins. Research using PARP16 antibodies has revealed its overexpression in certain cancers, including glioblastoma and hepatocellular carcinoma, highlighting its relevance in tumorigenesis and therapy resistance. Additionally, PARP16 inhibitors are emerging as candidates for targeted cancer treatments, underscoring the antibody’s utility in both basic research and drug development.
×