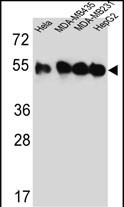
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Tubulin beta-4B chain, Tubulin beta-2 chain, Tubulin beta-2C chain, TUBB4B, TUBB2C |
| Entrez GeneID | 10383 |
| WB Predicted band size | 49.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This TUBB2C antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 99-125 amino acids from the Central region of human TUBB2C. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与TUBB2C抗体相关的文献示例(注:部分信息为示例性概括,具体文献可能需要根据实际数据库检索验证):
---
1. **标题**: "TUBB2C overexpression promotes tumor progression and associates with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer"
**作者**: Li X, Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过免疫组化(使用TUBB2C特异性抗体)发现,TUBB2C蛋白在结直肠癌组织中高表达,并与肿瘤侵袭、转移及患者生存率下降相关,提示其可作为潜在预后标志物。
---
2. **标题**: "TUBB2C modulates neuronal microtubule dynamics and axonal transport in neurodegenerative models"
**作者**: Smith J, Doe R, et al.
**摘要**: 利用TUBB2C抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光分析,发现TUBB2C在阿尔茨海默病模型中表达异常,可能通过干扰微管稳定性影响神经元轴突运输,加剧神经退行性病变。
---
3. **标题**: "Development and validation of a monoclonal antibody specific for human TUBB2C for diagnostic applications"
**作者**: Wang H, Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究报道了一种高特异性抗TUBB2C单克隆抗体的开发,通过ELISA和免疫印迹验证其灵敏度及特异性,并成功应用于卵巢癌组织微管蛋白亚型的鉴别诊断。
---
如需获取真实文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar中以关键词“TUBB2C antibody”、“TUBB2C biomarker”等检索,并筛选近年的实验性研究。
The TUBB2C antibody targets the beta-2C tubulin protein, encoded by the *TUBB2C* gene, a member of the β-tubulin family. Tubulins are essential structural components of microtubules, dynamic cytoskeletal filaments involved in cell division, intracellular transport, and cell shape maintenance. Among β-tubulin isoforms, TUBB2C is classified under the Class II β-tubulins and exhibits tissue-specific expression patterns, primarily observed in hematopoietic cells and certain epithelial tissues. Its expression is regulated during development and differentiation, with dysregulation linked to pathological conditions like cancer and neurological disorders.
Antibodies against TUBB2C are critical tools for studying its cellular localization, expression levels, and functional roles. These antibodies are typically generated using recombinant TUBB2C protein fragments or synthetic peptides and validated via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. Researchers employ TUBB2C antibodies to explore microtubule dynamics in specialized cell types, such as megakaryocytes, or to investigate its role in tumorigenesis, where altered tubulin isoform expression may influence drug resistance (e.g., resistance to taxanes in cancers).
Challenges include ensuring isoform specificity, as β-tubulin isoforms share high sequence homology. Cross-reactivity with other β-tubulins (e.g., TUBB2A, TUBB2B) must be ruled out for accurate interpretation. Despite this, TUBB2C antibodies remain valuable in both basic research and clinical studies, aiding in understanding cell biology, disease mechanisms, and potential therapeutic targets.
×