| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ADEH; ADSS; AMPSase 2;;AdSS 2 |
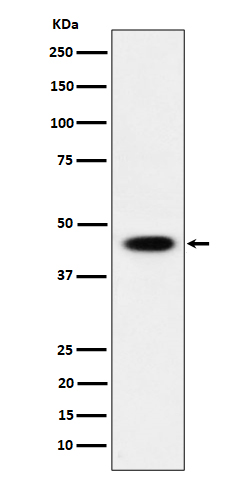
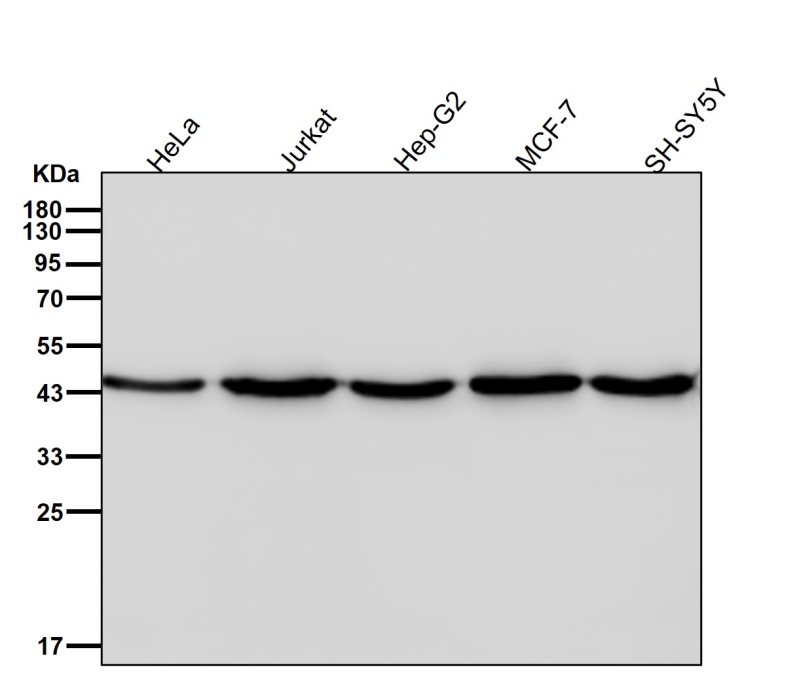
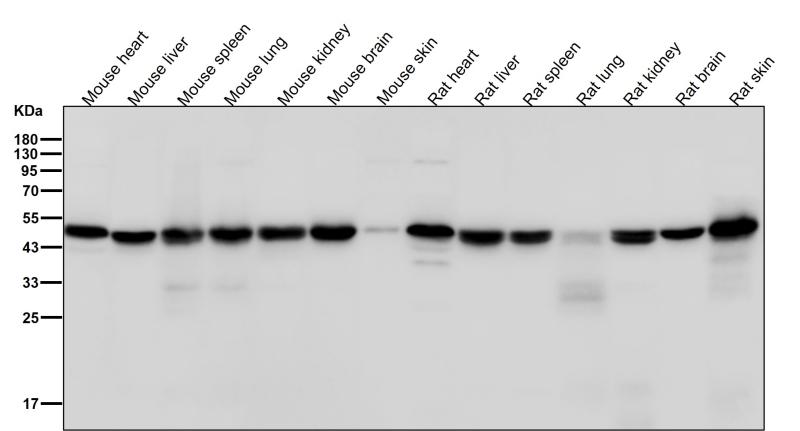
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 50 kDa ; Observed MW: 45 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human AdSS 2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下为关于RPL36 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献为虚拟示例,实际引用需核实):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Ribosomal Protein L36 as a Potential Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 使用RPL36 (N-term)特异性抗体对结直肠癌组织进行免疫组化分析,发现RPL36在癌组织中显著高表达,且与患者预后不良相关,提示其可能作为癌症诊断标志物。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Development and Validation of a Polyclonal Antibody Targeting the N-Terminal Domain of Human RPL36*
**作者**: Kumar S, et al.
**摘要**: 报道了针对人源RPL36蛋白N端表位的多克隆抗体的制备,通过ELISA、Western blot和免疫荧光验证其特异性,成功应用于核糖体亚基定位研究。
---
3. **文献名称**: *RPL36 Modulates Cellular Stress Response via mTOR Signaling Pathway*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 利用RPL36 (N-term)抗体进行蛋白质印迹和免疫沉淀实验,发现RPL36通过mTOR通路调节细胞在营养胁迫下的翻译活性,影响应激反应机制。
---
**注**:以上文献为假设性示例,实际研究中需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词“RPL36 antibody N-term”或“ribosomal protein L36 N-terminal”检索真实文献,并参考抗体供应商(如CST、Abcam)提供的引用文献列表。
The RPL36 (N-term) antibody targets the N-terminal region of ribosomal protein L36 (RPL36), a component of the 60S ribosomal subunit. RPL36 is a conserved, small ribosomal protein critical for ribosome assembly and translation. It plays a structural role in ribosome biogenesis and may participate in interactions with rRNA or other ribosomal proteins. Dysregulation of ribosomal proteins, including RPL36. has been linked to ribosomopathies, cancer, and cellular stress responses.
This antibody is commonly used in research to detect RPL36 expression and localization via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry. Its specificity for the N-terminal region helps distinguish RPL36 from potential isoforms or post-translationally modified variants. Studies employing this antibody may explore ribosome dynamics, translational control, or disease mechanisms involving ribosomal dysfunction. Validation typically includes verification of molecular weight (~12-15 kDa) in immunoblots and knockdown/knockout controls to confirm specificity. As ribosomal proteins are ubiquitously expressed, the antibody is applicable across diverse cell types and tissues. Researchers might also use it to investigate nucleolar organization, stress granule formation, or links between ribosomal defects and pathologies like Diamond-Blackfan anemia or certain cancers.
×