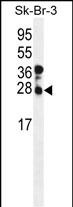
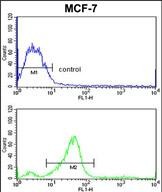
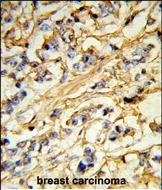
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Charged multivesicular body protein 4b, Chromatin-modifying protein 4b, CHMP4b, SNF7 homolog associated with Alix 1, SNF7-2, hSnf7-2, Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 32-2, Vps32-2, hVps32-2, CHMP4B, C20orf178, SHAX1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 128866 |
| WB Predicted band size | 25.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CHMP4B antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 51-79 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human CHMP4B. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CHMP4B (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概述:
---
1. **文献名称**: "ESCRT-III recognition by VPS4 ATPases"
**作者**: Obita, T., et al.
**摘要**: 本研究解析了ESCRT-III复合体中CHMP4B蛋白的N端结构域与VPS4 ATP酶的相互作用机制,利用针对CHMP4B N端的特异性抗体,通过免疫共沉淀实验验证了二者的直接结合,揭示了ESCRT-III在膜重塑中的分子调控途径。
---
2. **文献名称**: "CHMP4B is required for both midbody abscission and viral budding"
**作者**: Morita, E., et al.
**摘要**: 作者通过构建CHMP4B的N端特异性抗体,证明其在哺乳动物细胞分裂末期“中间体断裂”过程中的关键作用。抗体阻断实验显示,CHMP4B的N端结构域缺失会破坏ESCRT-III复合体的组装,导致细胞分裂异常和病毒颗粒释放缺陷。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Mutations in CHMP4B alter its oligomerization and disrupt endosomal sorting"
**作者**: Shim, S., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用针对CHMP4B N端的多克隆抗体,发现特定突变会干扰其寡聚化能力,导致内体分选功能障碍。Western blot和免疫荧光实验表明,CHMP4B的N端对其在ESCRT-III中的自组装及溶酶体靶向蛋白降解至关重要。
---
**备注**:若需更近期文献或具体应用场景的论文,建议在PubMed或Web of Science中检索关键词“CHMP4B antibody N-terminal”或结合研究领域(如癌症、神经退行性疾病)进一步筛选。
The CHMP4B (Charged Multivesicular Body Protein 4B) antibody targets the N-terminal region of the CHMP4B protein, a key component of the ESCRT-III (Endosomal Sorting Complex Required for Transport III) complex. CHMP4B plays a critical role in membrane remodeling processes, including cytokinesis, multivesicular body (MVB) formation, viral budding, and nuclear envelope reformation. As part of the ESCRT machinery, it facilitates the sorting of ubiquitinated cargo into intraluminal vesicles and mediates membrane scission events through its ability to polymerize into helical filaments that constrict membranes.
The N-terminal region of CHMP4B is essential for its oligomerization and interaction with other ESCRT-III subunits, such as CHMP2A and CHMP3. as well as regulatory proteins like VPS4 ATPase. Antibodies against the N-terminus are widely used to study CHMP4B's localization, expression levels, and functional dynamics in cellular processes. They are employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to investigate ESCRT-III dysfunction linked to diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and cytokinesis failure. Mutations in CHMP4B have been associated with congenital anomalies (e.g., cataracts) and impaired cell division, underscoring its biomedical relevance. These antibodies serve as vital tools for dissecting membrane trafficking mechanisms and pathological mechanisms in ESCRT-related diseases.
×