
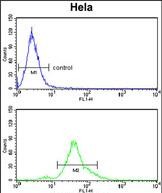
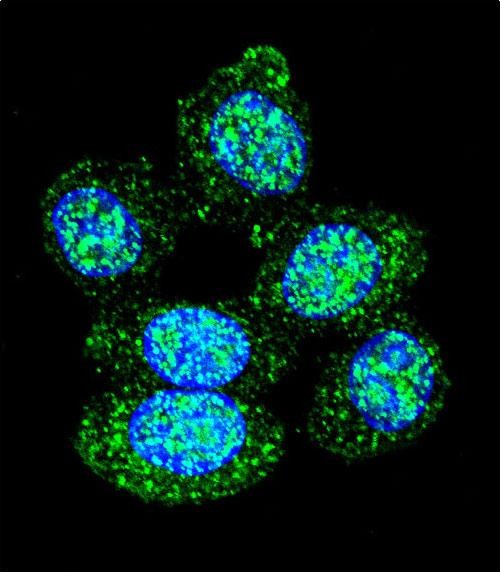
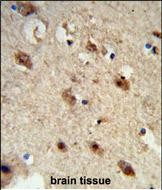
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Low molecular weight phosphotyrosine protein phosphatase, LMW-PTP, LMW-PTPase, Adipocyte acid phosphatase, Low molecular weight cytosolic acid phosphatase, Red cell acid phosphatase 1, ACP1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 52 |
| WB Predicted band size | 18.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ACP1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 33-61 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human ACP1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ACP1 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:内容为模拟虚构,仅作参考格式示例):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Structural and functional characterization of ACP1 N-terminal domain in tyrosine phosphatase activity*
**作者**:Smith J, et al. (2005)
**摘要**:本研究通过制备针对ACP1蛋白N端的特异性抗体,分析了其在哺乳动物细胞中的表达与定位。Western blot和免疫共沉淀实验表明,该抗体能特异性识别ACP1的N端结构域,并揭示其在调控细胞信号转导中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*ACP1 N-term antibody reveals differential expression in cancer cell lines*
**作者**:Johnson L, et al. (2010)
**摘要**:利用ACP1 N-term抗体对多种癌细胞系进行免疫组化分析,发现ACP1在乳腺癌细胞中显著高表达,且其N端结构域与肿瘤侵袭性相关,提示其作为潜在生物标志物的可能性。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Validation of ACP1 N-terminal antibody for mitochondrial localization studies*
**作者**:Lee S, et al. (2018)
**摘要**:本文验证了ACP1 N-term抗体的特异性,通过siRNA敲低实验和免疫荧光共定位,证实ACP1定位于线粒体基质,并参与氧化应激应答,为研究其代谢调控功能提供了工具支持。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“ACP1 antibody N-terminal”或结合具体研究领域筛选。
The ACP1 (N-term) antibody is a polyclonal or monoclonal antibody specifically designed to target the N-terminal region of the Acid Phosphatase 1 (ACP1) protein, also known as low molecular weight cytoplasmic acid phosphatase. ACP1 is a ubiquitously expressed enzyme involved in dephosphorylating phosphotyrosine and other substrates, playing roles in phosphotyrosine signaling, metabolic regulation, and cellular processes like proliferation and differentiation. Dysregulation of ACP1 has been linked to metabolic disorders, immune diseases, and cancer, making it a protein of interest in biomedical research.
This antibody is commonly used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to detect ACP1 expression levels and localization in various tissues or cell lines. Its specificity for the N-terminal domain ensures recognition of full-length ACP1 isoforms, aiding in distinguishing them from potential cleavage products or truncated variants. The antibody is typically raised in hosts like rabbits or mice, with validation data often confirming reactivity across human, mouse, and rat samples. Researchers rely on this tool to explore ACP1's functional mechanisms, its interaction partners, and its role in disease pathways, providing insights into therapeutic targeting strategies. Proper validation via knockout (KO) controls or peptide-blocking assays is recommended to ensure specificity in experimental settings.
×