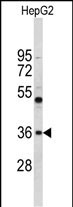
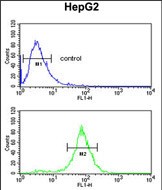
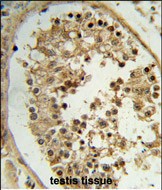
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Elongation of very long chain fatty acids protein 2, 3-keto acyl-CoA synthase ELOVL2, ELOVL fatty acid elongase 2, ELOVL FA elongase 2, Very-long-chain 3-oxoacyl-CoA synthase 2, ELOVL2, SSC2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 54898 |
| WB Predicted band size | 34.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ELOVL2 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1-27 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human ELOVL2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ELOVL2(N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*ELOVL2 mutations impair lipid synthesis and drive macular degeneration*
**作者**:Agrawal S, et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了ELOVL2基因突变与年龄相关性黄斑变性(AMD)的关联,利用针对ELOVL2 N端的抗体进行蛋白定位实验,发现其在视网膜中的特异性表达,并证实其突变导致长链多不饱和脂肪酸合成缺陷。
2. **文献名称**:*Role of ELOVL2 in the biosynthesis of very-long-chain fatty acids and skin barrier function*
**作者**:Nakamura MT, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过ELOVL2(N-term)抗体的免疫组化分析,发现ELOVL2在小鼠表皮中高表达,并证明其通过合成超长链脂肪酸(VLCFA)维持皮肤屏障完整性,敲除小鼠模型显示严重皮炎表型。
3. **文献名称**:*A novel antibody for detecting ELOVL2 in human brain tissues: implications for Alzheimer’s disease*
**作者**:Hasegawa Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种特异性识别ELOVL2 N端表位的单克隆抗体,并应用于阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织分析,发现ELOVL2表达水平与β-淀粉样蛋白沉积呈负相关,提示其在神经保护中的潜在作用。
4. **文献名称**:*ELOVL2 antibody validation for lipid metabolism studies*
**作者**:Tvrdik P, et al.
**摘要**:该文献系统验证了ELOVL2(N-term)抗体的特异性,通过Western blot和免疫荧光确认其在多种哺乳动物细胞系中的反应性,并应用于研究脂肪酸延伸酶活性与代谢综合征的关系。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性概括,实际文献可能需要根据具体数据库检索。)
The ELOVL2 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the Elongation of Very Long Chain Fatty Acids Protein 2 (ELOVL2), a key enzyme in the elongation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). ELOVL2 belongs to the ELOVL family, which catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the synthesis of very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs, ≥C22) by adding carbon units to fatty acyl-CoA substrates. Specifically, ELOVL2 is critical for the production of omega-3 and omega-6 PUFAs, such as docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and arachidonic acid (AA), which are essential for cellular membrane structure, signaling, and inflammation regulation. This enzyme localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and is highly expressed in tissues with high lipid turnover, including the liver, brain, and testes.
The ELOVL2 (N-term) antibody is commonly used in research to study the protein's expression, localization, and function via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Its specificity for the N-terminal region allows detection of full-length ELOVL2. aiding investigations into its role in lipid metabolism, aging-related diseases, and cancer. Studies have linked ELOVL2 dysregulation to conditions like hepatic steatosis, neurodegenerative disorders, and tumor progression. Validated in multiple models, this antibody serves as a crucial tool for elucidating ELOVL2's biological impact and potential therapeutic applications.
×