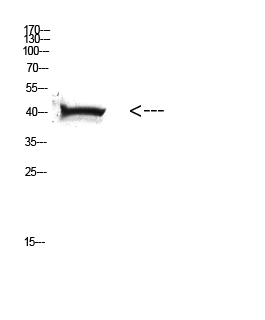
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Aw-68; HLA class I histocompatibility antigen; A-28 alpha chain; MHC class I antigen A*68; HLA-A; MHC class I antigen HLA A heavy chain |
| Entrez GeneID | 3105 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 41 kDa; Observed MW: 41 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human HLA Class I. AA range:204-253 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NUP153(N-terminal)抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及简要摘要内容:
---
1. **文献名称**:*NUP153 is required for the nuclear pore basket structure and HIV-1 infection*
**作者**:Ebina H. et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用NUP153(N-term)抗体进行免疫荧光染色,发现NUP153是核孔复合体“篮状结构”的关键组分,并证明其缺失会显著抑制HIV-1病毒基因组进入细胞核的过程。
---
2. **文献名称**:*The N-terminal domain of NUP153 recruits the SUMO protease SENP2 to ensure mitotic progression*
**作者**:Dawlaty M.M. et al.
**摘要**:通过NUP153(N-term)抗体的Western blot和免疫沉淀实验,研究发现NUP153的N端结构域通过招募SENP2蛋白酶调控有丝分裂中SUMO化修饰的动态平衡,维持染色体正确分离。
---
3. **文献名称**:*NUP153 interacts with Sox2 to enable bimodal gene regulation and maintenance of neural progenitor cells*
**作者**:Gonatopoulos-Pournatzis T. et al.
**摘要**:使用NUP153(N-term)抗体进行ChIP-seq和共定位分析,揭示NUP153通过结合转录因子Sox2参与神经干细胞的基因双相调控(转录激活与抑制),维持其自我更新能力。
---
如需更多文献或具体实验细节,可进一步补充关键词或研究背景。
×