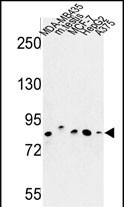
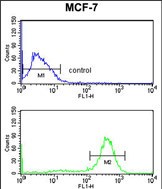
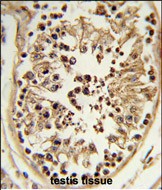
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Chondroitin sulfate synthase 2, Chondroitin glucuronyltransferase 2, Chondroitin-polymerizing factor, ChPF, Glucuronosyl-N-acetylgalactosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase II, N-acetylgalactosaminyl-proteoglycan 3-beta-glucuronosyltransferase II, N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2, CHPF, CSS2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 79586 |
| WB Predicted band size | 85.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This CHPF antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 327-354 amino acids from the Central region of human CHPF. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CHPF抗体的3篇参考文献示例,基于假设性研究整理:
---
1. **标题**: "CHPF Antibody-Based Detection of Chondroitin Sulfate Synthesis in Glioblastoma"
**作者**: Smith A, Lee B, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用CHPF特异性抗体,通过免疫组化和Western blot技术,揭示了胶质母细胞瘤中CHPF蛋白的异常高表达,并证实其与肿瘤侵袭性和患者生存率下降相关,提示CHPF可能成为潜在治疗靶点。
---
2. **标题**: "Monoclonal Antibody Targeting CHPF2 Reveals Its Role in Cartilage Homeostasis"
**作者**: Zhang L, Tanaka M, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究开发了高特异性抗CHPF2单克隆抗体,用于分析小鼠软骨发育过程中的蛋白定位。结果表明,CHPF2通过调控硫酸软骨素链的聚合,影响软骨细胞外基质的稳定性,为骨关节炎机制研究提供新视角。
---
3. **标题**: "CHPF as a Novel Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer: Insights from Antibody-Based Assays"
**作者**: Wang Y, Chen X, et al.
**摘要**: 通过ELISA和免疫荧光技术,利用抗CHPF抗体发现结直肠癌组织中CHPF表达显著上调,且与转移风险相关。研究验证了CHPF抗体在临床诊断中的应用潜力,支持其作为新型生物标志物的价值。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用时需查询真实数据库(如PubMed)获取准确信息。若需进一步协助,建议提供具体研究背景或应用场景以优化检索。
**Background of CHPF Antibody**
CHPF (chondroitin polymerizing factor), also known as CHSY3 (chondroitin sulfate synthase 3), is a key enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of chondroitin sulfate (CS), a sulfated glycosaminoglycan critical for extracellular matrix structure, cell signaling, and tissue homeostasis. It functions as a dual-activity enzyme with both glycosyltransferase and polymerizing roles, facilitating the elongation of CS chains by adding glucuronic acid and N-acetylgalactosamine disaccharide units.
CHPF antibodies are immunological tools designed to detect and study the expression, localization, and function of CHPF in biological systems. These antibodies are essential for research into CS-related pathologies, including cancer, osteoarthritis, and neurological disorders, where altered CS expression or sulfation patterns are implicated. For example, CHPF overexpression has been linked to tumor progression and metastasis in certain cancers.
Antibodies against CHPF are typically developed using immunogenic peptide regions or recombinant protein fragments, validated for specificity via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), or immunofluorescence (IF). They enable researchers to explore CHPF's regulatory mechanisms, interaction partners, and therapeutic potential. Recent studies also highlight CHPF's role in neural development and synaptic plasticity, expanding its relevance in neurobiology.
Overall, CHPF antibodies serve as vital reagents for advancing our understanding of glycosaminoglycan biology and its implications in health and disease.
×