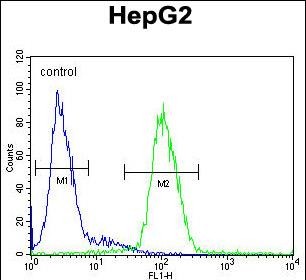
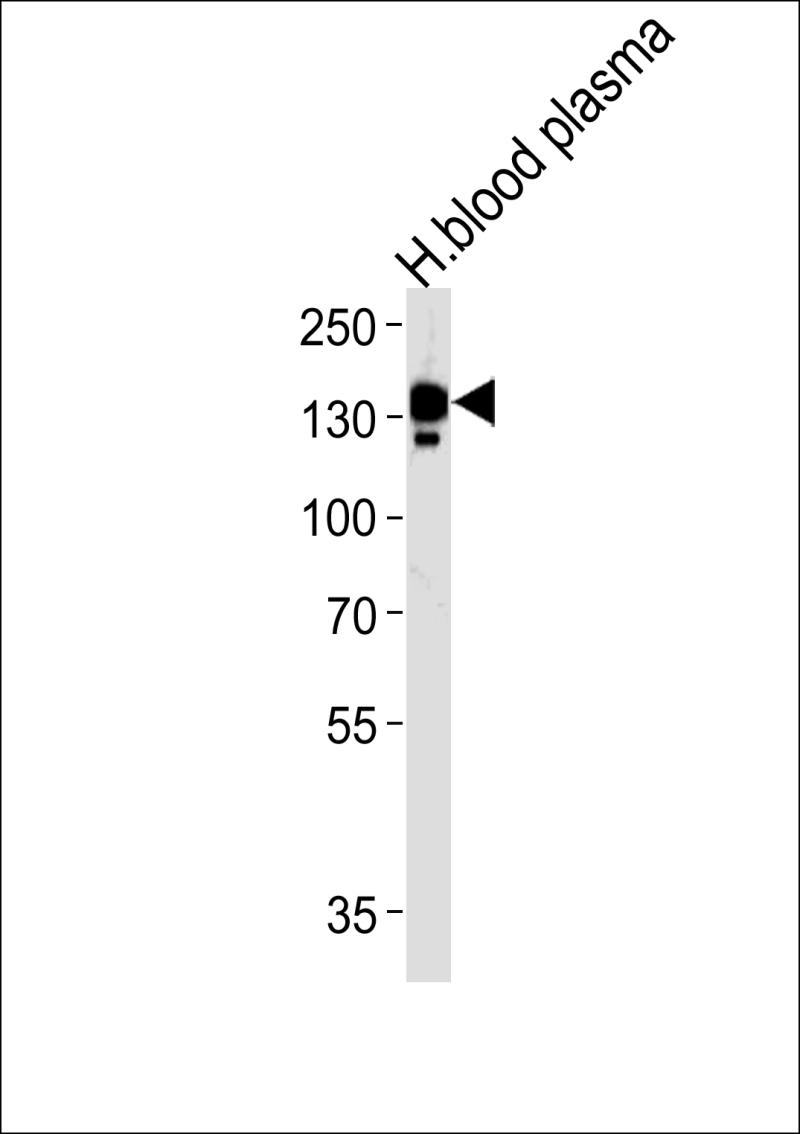
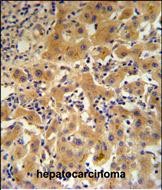
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Ceruloplasmin, Ferroxidase, CP |
| Entrez GeneID | 1356 |
| WB Predicted band size | 122.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This CP antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 121-151 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human CP. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于CP(N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容的简要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Antibodies specific for caspase-cleaved poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase*
**作者**:Cohen, G. M. et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种特异性识别caspase切割后产生的PARP(聚ADP核糖聚合酶)N末端片段的抗体。该抗体能选择性检测凋亡细胞中PARP的切割形式,为细胞凋亡的分子机制研究提供了工具。
---
2. **文献名称**:*N-terminal antibodies for detection of ubiquitin-proteasome system substrates*
**作者**:Hershko, A. & Ciechanover, A.
**摘要**:文章探讨了针对泛素化蛋白N末端的抗体在蛋白质降解研究中的应用。作者通过免疫印迹验证了抗体对泛素化底物的特异性,并用于监测蛋白酶体依赖的蛋白降解过程。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Proteolytic processing of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid precursor protein analyzed by N-terminal-specific antibodies*
**作者**:Haass, C. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用N端特异性抗体分析阿尔茨海默病中淀粉样前体蛋白(APP)的酶切过程,揭示了β-和γ-分泌酶的切割位点及病理相关性,为疾病机制提供了新见解。
---
这些文献展示了CP(N-term)抗体在细胞凋亡、蛋白质降解及疾病研究中的关键作用,涵盖特异性检测、功能验证及疾病模型应用。
The CP (N-term) antibody is a specialized immunological tool designed to target the N-terminal region of proteins containing a specific cyclic peptide (CP) motif. This antibody is particularly valuable in proteomics and biochemical research, where precise detection of protein isoforms or post-translational modifications (PTMs) near the N-terminus is critical. The N-terminal region often plays essential roles in protein stability, localization, and interaction, making antibodies against this domain crucial for studying protein function.
CP (N-term) antibodies are typically generated by immunizing animals with synthetic peptides corresponding to the N-terminal sequence of the target protein, often conjugated to carrier proteins to enhance immunogenicity. They are rigorously validated using techniques like western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to ensure specificity. These antibodies are widely used to investigate proteolytic processing (e.g., cleavage by proteases), truncation mutations, or N-terminal modifications (e.g., acetylation, ubiquitination).
In disease research, CP (N-term) antibodies help identify biomarkers associated with conditions like cancer or neurodegenerative disorders, where altered protein processing is common. Their ability to distinguish full-length proteins from truncated forms makes them indispensable for mechanistic studies. However, cross-reactivity with unrelated proteins sharing similar N-terminal sequences remains a potential challenge, emphasizing the need for careful experimental controls. Overall, CP (N-term) antibodies are vital tools for dissecting protein dynamics and molecular pathways.
×