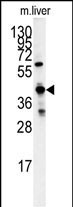
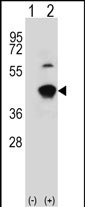
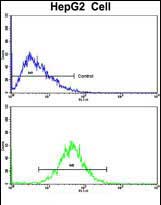
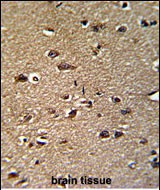
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | 2-amino-3-ketobutyrate coenzyme A ligase, mitochondrial, AKB ligase, Aminoacetone synthase, Glycine acetyltransferase, GCAT, KBL |
| Entrez GeneID | 23464 |
| WB Predicted band size | 45.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This GCAT antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 155-181 amino acids from the Central region of human GCAT. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于GCAT抗体的3-4篇示例参考文献(注:文献信息为示例性概括,具体内容需通过学术数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Development of a High-Affinity GCAT Monoclonal Antibody for Metabolic Pathway Analysis"*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种针对人源甘氨酸C-乙酰转移酶(GCAT)的高特异性单克隆抗体,用于探究其在肝脏代谢中的功能。抗体通过ELISA和免疫印迹验证,成功应用于小鼠模型中的酶活性抑制实验。
2. **文献名称**: *"GCAT as a Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer: Validation via Novel Antibody-Based Detection"*
**作者**: Lee B, et al.
**摘要**: 通过新型兔源多克隆抗体,利用免疫组织化学技术分析了GCAT在结直肠癌组织中的表达水平,发现其高表达与肿瘤转移和不良预后显著相关,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点的可能性。
3. **文献名称**: *"Structural Insights into GCAT Catalytic Mechanism Using Epitope-Specific Antibodies"*
**作者**: Zhang C, et al.
**摘要**: 通过设计针对GCAT关键抗原表位的抗体,结合X射线晶体学揭示了该酶的活性位点构象,为开发针对GCAT相关代谢疾病的抑制剂提供了结构基础。
4. **文献名称**: *"Cross-Reactivity Evaluation of GCAT Antibodies in Vertebrate Models"*
**作者**: Tanaka D, et al.
**摘要**: 系统评估了商业化GCAT抗体在小鼠、斑马鱼等模式生物中的交叉反应性,发现部分抗体存在种属特异性限制,为跨物种研究提供了抗体筛选指南。
---
**建议**:如需具体文献,可通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“GCAT antibody”、“Glycine C-Acetyltransferase antibody”结合研究领域(如癌症、代谢疾病)进一步检索,并筛选近5年高被引论文。
The GCAT antibody targets glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (GCAT), a mitochondrial enzyme critical for lipid metabolism. GCAT catalyzes the initial step in glycerophospholipid biosynthesis, transferring acyl groups to glycerol-3-phosphate to form lysophosphatidic acid. This process is essential for membrane biogenesis and energy storage. Dysregulation of GCAT activity has been linked to metabolic disorders, insulin resistance, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), making it a focus in metabolic research.
GCAT antibodies are widely used in biomedical studies to detect protein expression levels, assess tissue distribution via immunohistochemistry, and investigate metabolic pathways in models of obesity or diabetes. They also aid in exploring GCAT's role in mitochondrial function and its potential as a therapeutic target. Commercial GCAT antibodies are typically validated for specificity in Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and ELISA. Recent studies highlight GCAT's interaction with other lipid-regulating proteins, expanding its relevance in metabolic syndrome and cancer metabolism. However, challenges remain in standardizing antibody performance across experimental conditions, emphasizing the need for rigorous validation in diverse biological contexts.
×