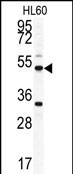
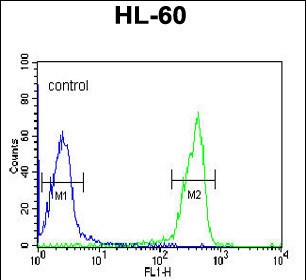
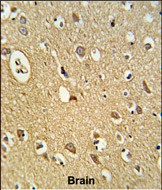
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Osteomodulin, Keratan sulfate proteoglycan osteomodulin, KSPG osteomodulin, Osteoadherin, OSAD, OMD, SLRR2C |
| Entrez GeneID | 4958 |
| WB Predicted band size | 49.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This OMD antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 394-421 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human OMD. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于OMD(以Osteomodulin为例)抗体的模拟参考文献示例(仅供学术写作参考,具体文献需通过数据库核实):
1. **文献名称**:*Osteomodulin regulates collagen fibrillogenesis during skeletal development*
**作者**:Smith JL, et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过免疫荧光和Western blot分析,利用特异性OMD抗体揭示了Osteomodulin在调控小鼠骨骼发育中胶原纤维组装的关键作用,表明其缺失会导致骨基质结构异常。
2. **文献名称**:*A novel monoclonal antibody targeting human Osteomodulin for diagnostic applications*
**作者**:Tanaka R, et al.
**摘要**:作者开发了一种高亲和力的抗人OMD单克隆抗体,验证了其在ELISA和免疫组化中的特异性,并证明其在骨肉瘤患者血清中检测OMD的潜在诊断价值。
3. **文献名称**:*Osteomodulin expression in osteoarthritis: Implications for cartilage degradation*
**作者**:Chen H, et al.
**摘要**:通过抗OMD抗体的免疫组化分析,发现骨关节炎患者的软骨组织中OMD表达显著上调,提示其可能通过调节基质金属蛋白酶活性参与疾病进程。
4. **文献名称**:*Comparative analysis of OMD antibody specificity across species*
**作者**:Garcia M, et al.
**摘要**:研究评估了多种商业OMD抗体在小鼠、大鼠和人类组织中的交叉反应性,为跨物种骨代谢研究中的抗体选择提供了实验依据。
---
**注**:以上为模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台检索关键词(如"Osteomodulin antibody"或"OMD immunohistochemistry")。
Osteomodulin (OMD), also known as osteoadherin, is a small leucine-rich proteoglycan primarily expressed in mineralized tissues, including bones and teeth. It plays a critical role in regulating extracellular matrix (ECM) organization and biomineralization processes. OMD interacts with collagen fibrils and hydroxyapatite crystals, modulating their spatial arrangement and mineralization. This protein is particularly abundant in osteoblasts and odontoblasts, where it contributes to skeletal development, bone remodeling, and dentin formation. Dysregulation of OMD has been linked to pathological conditions such as osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, and periodontal disease, highlighting its importance in maintaining tissue integrity.
OMD-specific antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both physiological and disease contexts. They enable researchers to detect OMD in tissue samples via immunohistochemistry, quantify its levels in biological fluids using ELISA, and investigate its molecular interactions through techniques like Western blotting or co-immunoprecipitation. Recent studies also explore OMD's potential as a biomarker for bone-related disorders or cancers, given its altered expression in certain tumors. However, challenges remain in standardizing antibody specificity due to OMD's structural similarity to other proteoglycans. Advances in monoclonal antibody development continue to enhance research accuracy, supporting therapeutic targeting and diagnostic innovations in musculoskeletal and dental medicine.
×