
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
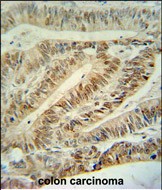
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
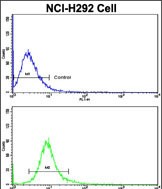
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Cullin-5, CUL-5, Vasopressin-activated calcium-mobilizing receptor 1, VACM-1, CUL5, VACM1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 8065 |
| WB Predicted band size | 91.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CUL5 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 747-774 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human CUL5. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CUL5抗体的代表性文献,简要概括内容如下:
1. **"HIV-1 Vif antagonizes the restriction activity of APOBEC3G by recruiting CUL5 to induce its ubiquitination and degradation"**
- **作者**: Yu X. et al. (2003)
- **摘要**: 研究发现HIV-1病毒蛋白Vif通过招募宿主CUL5形成E3泛素连接酶复合物(CRL5),靶向降解宿主抗病毒因子APOBEC3G,揭示CUL5在病毒逃逸宿主免疫中的作用机制。
2. **"Structure of the CUL5-ElonginB-ElonginC complex and its role in SOCS-box-mediated ubiquitination"**
- **作者**: Muniz J.R.C. et al. (2016)
- **摘要**: 通过冷冻电镜解析CUL5与Elongin B/C及SOCS-box蛋白的复合体结构,阐明CUL5在泛素化通路中的底物识别机制,为设计靶向CRL5的药物提供结构基础。
3. **"CUL5 promotes the development of gastric cancer through targeting cyclin E"**
- **作者**: Li Y. et al. (2018)
- **摘要**: 发现CUL5在胃癌中通过泛素化降解细胞周期蛋白Cyclin E,促进肿瘤细胞增殖,提示CUL5可能作为癌症治疗的潜在靶点。
4. **"Cullin 5 regulates viral defense and self-renewal in embryonic stem cells"**
- **作者**: Wu X. et al. (2020)
- **摘要**: 研究显示CUL5通过调控干扰素通路增强胚胎干细胞的抗病毒能力,同时参与干细胞的自我更新,揭示其在先天免疫和干细胞生物学中的双重功能。
以上文献涵盖CUL5在病毒-宿主互作、结构生物学、肿瘤发生及干细胞领域的功能研究,可作为相关抗体应用的理论参考。
The CUL5 (Cullin 5) antibody is a research tool designed to detect and study the CUL5 protein, a core component of the Cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase (CRL) family. CUL5 plays a critical role in the ubiquitin-proteasome system by facilitating the targeted degradation of specific substrates, thereby regulating cellular processes such as cell cycle progression, DNA repair, and signal transduction. Structurally, CUL5 acts as a scaffold protein, binding to adaptor proteins (e.g., SOCS box-containing proteins) and substrate receptors to form the CRL5 complex, which tags proteins with ubiquitin for proteasomal destruction.
CUL5 is notably involved in viral defense mechanisms and tumor suppression. For example, it interacts with viral proteins like HIV-1 Nef to counteract host antiviral responses and participates in degrading hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) under normoxic conditions. Dysregulation of CUL5 has been linked to cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and immune disorders. Researchers use CUL5 antibodies in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunoprecipitation (IP) to investigate its expression, localization, and interaction partners in various tissues or disease models. These studies aim to elucidate its role in cellular homeostasis and pathological conditions, offering insights for therapeutic targeting. Commercial CUL5 antibodies are typically validated for specificity and sensitivity across human, mouse, and rat samples.
×