
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
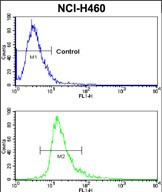
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor, CAR, hCAR, CVB3-binding protein, Coxsackievirus B-adenovirus receptor, HCVADR, CXADR, CAR |
| Entrez GeneID | 1525 |
| WB Predicted band size | 40.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CXADR antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 132-161 amino acids from the Central region of human CXADR. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于CXADR抗体的3篇参考文献,简明扼要地列出文献名称、作者及摘要内容:
---
1. **文献名称**: *The murine homolog of the coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor is a functional homolog in human cells*
**作者**: Hsu KH, Lonberg-Holm K, Alstein B, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究首次克隆并鉴定了小鼠CXADR受体,证明其功能与人类受体同源。通过特异性抗体的免疫定位实验,发现CXADR在细胞膜上介导腺病毒入侵,为后续病毒感染机制研究奠定基础。
2. **文献名称**: *Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor (CXADR) in myocardial tissues of patients with myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy*
**作者**: Noutsias M, Fechner H, de Jonge H, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化分析,研究者使用CXADR抗体检测心肌炎和扩张型心肌病患者的心脏组织,发现CXADR表达显著上调,提示其在病毒性心肌损伤中可能起关键作用。
3. **文献名称**: *CXADR as a prognostic biomarker in gastric cancer correlates with immune infiltration*
**作者**: Koike H, Kajita S.
**摘要**: 利用CXADR抗体对胃癌组织进行染色,发现CXADR高表达与患者预后不良相关。研究进一步分析了CXADR与肿瘤免疫微环境的关系,为靶向治疗提供潜在方向。
---
以上文献均涉及CXADR抗体的直接应用,涵盖病毒感染机制、心脏病理及肿瘤研究领域。如需更多文献扩展,可进一步检索近年基于CXADR抗体在免疫治疗或单细胞测序中的研究。
CXADR (Coxsackievirus and Adenovirus Receptor) is a transmembrane protein that serves as a primary receptor for coxsackievirus B (CVB) and adenoviruses, facilitating their cellular entry. It plays a dual role in viral pathogenesis and cellular adhesion, contributing to tissue barrier integrity by forming homophilic interactions at tight junctions. CXADR is widely expressed in epithelial and endothelial cells, particularly in the heart, brain, pancreas, and gastrointestinal tract.
CXADR antibodies are essential tools for studying its biological functions, viral entry mechanisms, and disease associations. In research, these antibodies are used in techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and flow cytometry to detect CXADR expression, localization, and regulation. Dysregulation of CXADR has been linked to pathologies such as myocarditis (due to CVB infection), pancreatitis, and certain cancers, where its overexpression or loss may influence tumor progression or viral susceptibility.
Additionally, CXADR antibodies have therapeutic potential. Neutralizing antibodies can block viral attachment, offering strategies for antiviral therapies. They also aid in exploring CXADR's role in non-infectious conditions, including autoimmune diseases and tissue remodeling. However, challenges remain in understanding tissue-specific functions and balancing therapeutic targeting to avoid disrupting physiological roles. Ongoing research aims to refine antibody specificity and evaluate clinical applications.
×