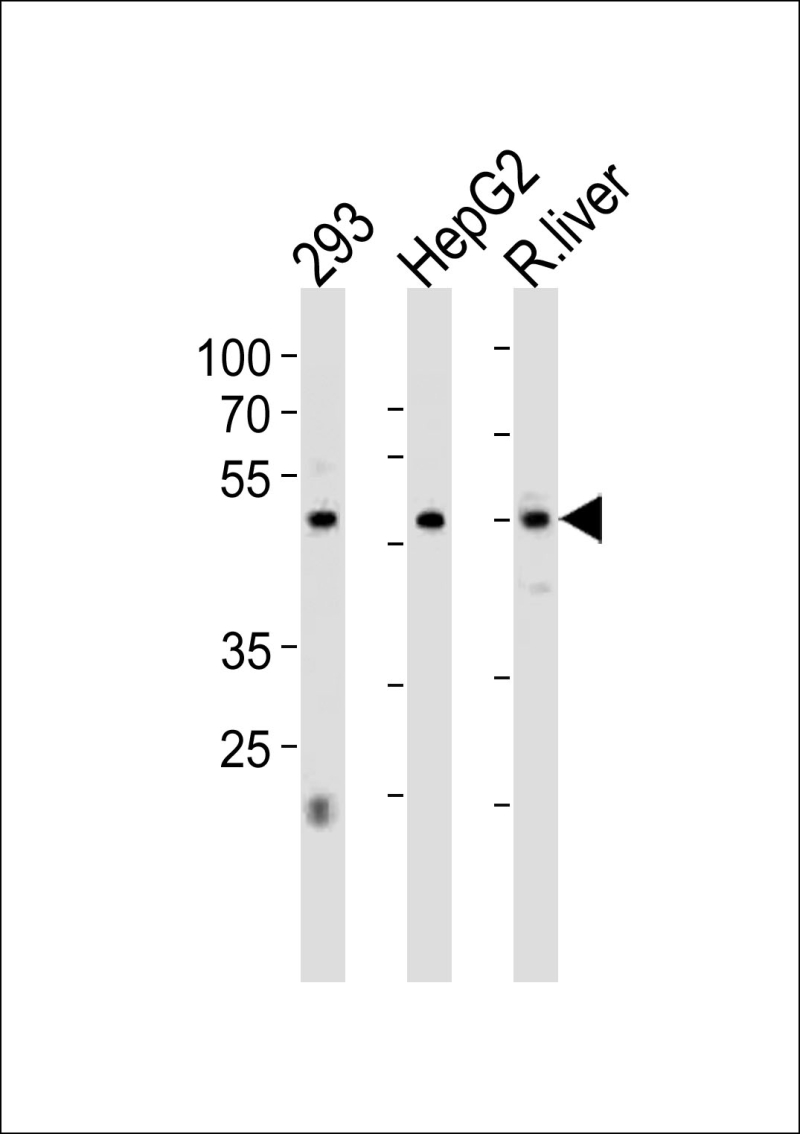
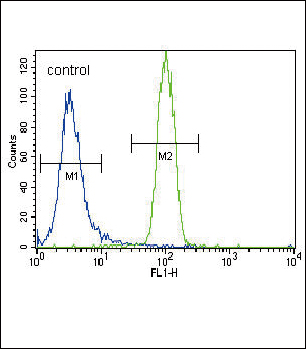
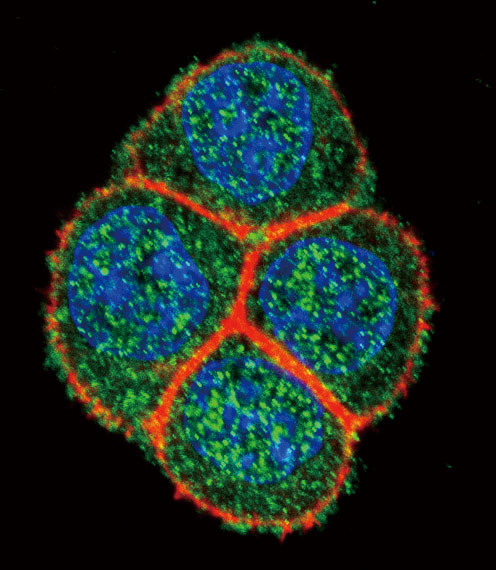
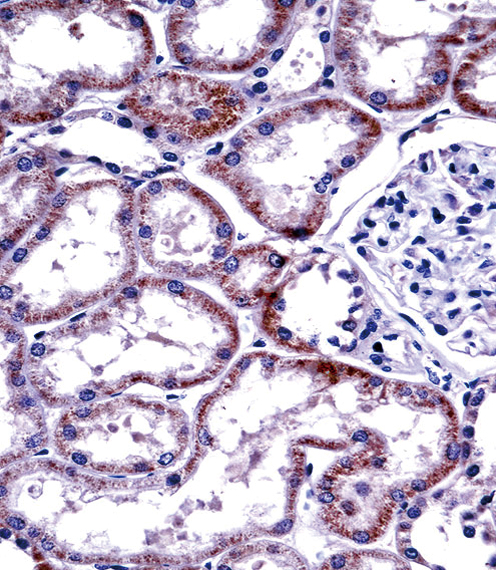
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha, HNF-4-alpha, Nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group A member 1, Transcription factor 14, TCF-14, Transcription factor HNF-4, HNF4A, HNF4, NR2A1, TCF14 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3172 |
| WB Predicted band size | 52.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Rat |
| Immunogen | This HNF4A antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 281-312 amino acids from the Central region of human HNF4A. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于HNF4A抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要(信息基于公开研究整理):
1. **文献名称**:*"Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (HNF4α) regulates intestinal epithelial cell proliferation and apical junctional complex assembly*"
**作者**:Babeu JP et al.
**摘要**:研究利用HNF4A特异性抗体(Western blot和免疫荧光)揭示其在肠道上皮细胞增殖和细胞间连接中的作用,表明HNF4A缺失导致肠道屏障功能异常。
2. **文献名称**:*"HNF4A haploinsufficiency in MODY1 alters human pancreatic β-cell transcriptional landscape*"
**作者**:Wang H et al.
**摘要**:通过ChIP-seq结合HNF4A抗体,发现MODY1糖尿病中HNF4A结合位点减少,导致胰岛素分泌相关基因表达下调,强调了HNF4A在β细胞功能中的调控机制。
3. **文献名称**:*"Antibody-based validation of extracellular HNF4A isoforms in hepatocellular carcinoma*"
**作者**:Santangelo L et al.
**摘要**:开发特异性HNF4A抗体区分不同亚型,证实肝癌细胞中异常表达的胞外HNF4A异构体可能作为潜在生物标志物,为靶向治疗提供依据。
如需具体DOI或期刊信息,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“HNF4A antibody” + 应用场景(如ChIP/Western/IHC)进一步检索。
**Background of HNF4A Antibody**
HNF4A (Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4 Alpha) is a transcription factor belonging to the nuclear receptor superfamily, primarily expressed in the liver, pancreas, kidney, and intestines. It plays a critical role in regulating tissue-specific gene expression, particularly genes involved in lipid and glucose metabolism, drug detoxification, and cellular differentiation. Mutations in *HNF4A* are linked to monogenic diabetes (MODY1), hepatic dysfunction, and certain cancers, underscoring its importance in metabolic homeostasis and disease pathogenesis.
HNF4A antibodies are essential tools for studying the expression, localization, and functional roles of HNF4A in both normal and pathological contexts. These antibodies are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to detect HNF4A protein levels, assess its nuclear localization, and map its DNA-binding activity. Due to the existence of multiple HNF4A isoforms generated by alternative splicing or promoter usage, antibody specificity is crucial to distinguish between variants, which may exhibit divergent regulatory functions.
Research applications include investigating developmental biology, metabolic disorders, cancer mechanisms, and gene regulatory networks. Commercially available HNF4A antibodies are typically raised against epitopes within conserved regions, such as the DNA-binding domain (DBD) or ligand-binding domain (LBD), and require validation in relevant experimental systems to ensure reliability. Their use has significantly advanced understanding of HNF4A's role in organ development, disease progression, and transcriptional regulation.
×