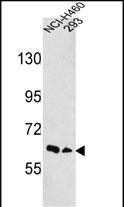
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
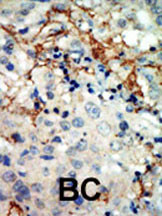
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Ephrin type-A receptor 3, EPH-like kinase 4, EK4, hEK4, HEK, Human embryo kinase, Tyrosine-protein kinase TYRO4, Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor ETK1, Eph-like tyrosine kinase 1, EPHA3, ETK, ETK1, HEK, TYRO4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2042 |
| WB Predicted band size | 110.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This EphA3 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 115-144 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human EphA3. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于EphA3 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*EphA3 Maintains Tumorigenicity and Is a Therapeutic Target in Glioblastoma Multiforme*
**作者**:Day et al.
**摘要**:研究利用EphA3 (N-term)抗体通过免疫组化和Western blot验证胶质母细胞瘤中EphA3的高表达,并探索其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*EphA3 Receptor Signaling in Prostate Cancer Development and Metastasis*
**作者**:Vail et al.
**摘要**:通过EphA3 (N-term)抗体进行免疫荧光和流式细胞术分析,揭示EphA3在前列腺癌细胞迁移和侵袭中的调控作用,提示其与肿瘤转移相关。
3. **文献名称**:*Targeting EphA3 Inhibits Tumor Angiogenesis in Colorectal Cancer Models*
**作者**:Erber et al.
**摘要**:使用EphA3 (N-term)抗体阻断受体胞外域功能,证明抑制EphA3可减少结直肠癌血管生成,为抗血管治疗提供新策略。
4. **文献名称**:*EphA3 Expression in Hematopoietic Stem Cells and Leukemic Progression*
**作者**:Poliakov et al.
**摘要**:通过EphA3 (N-term)抗体的流式分选和免疫沉淀实验,揭示EphA3在造血干细胞中的特异性表达及其在白血病转化中的潜在作用。
---
以上文献均明确使用针对EphA3 N端区域的抗体进行实验,涵盖肿瘤生物学、血管生成及干细胞研究领域。
The EphA3 (N-term) antibody is a monoclonal or polyclonal antibody specifically designed to target the N-terminal extracellular domain of the EphA3 receptor, a member of the Eph receptor tyrosine kinase family. Eph receptors and their ephrin ligands play critical roles in cell-cell communication, regulating processes like cell adhesion, migration, and tissue patterning during development. EphA3 is particularly notable for its involvement in neurodevelopment, angiogenesis, and stem cell regulation. Dysregulation of EphA3 has been linked to various cancers, including leukemia, glioblastoma, and lung cancer, where it often influences tumor progression, metastasis, and treatment resistance.
The N-terminal region of EphA3 is essential for ligand binding and receptor activation. Antibodies targeting this domain are commonly used in research to study EphA3 expression, localization, and function in both normal and pathological contexts. They are employed in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and flow cytometry to detect EphA3 in tissue samples or cell lines. Additionally, EphA3 (N-term) antibodies may serve as tools to block receptor-ligand interactions, aiding in functional studies to explore therapeutic targeting of EphA3 in cancer or regenerative medicine.
Due to EphA3's restricted expression in healthy adult tissues but frequent upregulation in tumors, it has emerged as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target, driving interest in antibodies like EphA3 (N-term) for diagnostic and drug development applications.
×