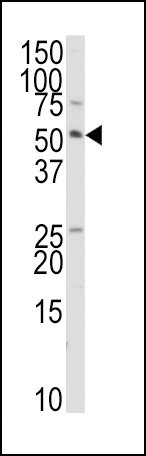
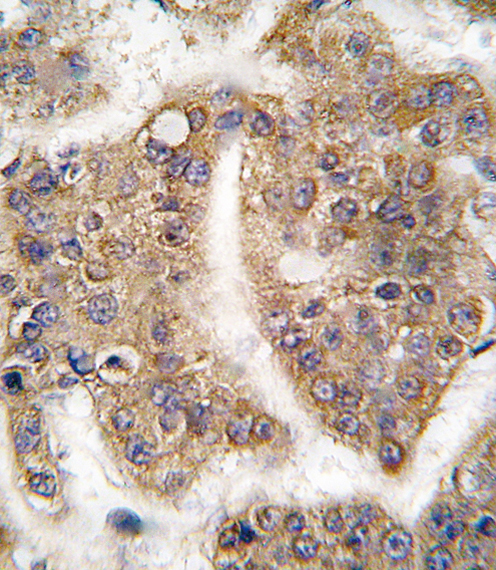
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRAIP, 632-, RING finger protein 206, TRAF-interacting protein, TRAIP, RNF206, TRIP |
| Entrez GeneID | 10293 |
| WB Predicted band size | 53.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This TRAIP antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 328-356 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human TRAIP. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及TRAIP抗体的代表性文献,涵盖功能机制及疾病关联研究:
---
1. **文献名称**:*TRAIP promotes DNA damage response during genome replication and is mutated in primordial dwarfism*
**作者**:Harley, J. et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用TRAIP抗体进行免疫荧光和Western blot实验,发现TRAIP蛋白在DNA复制压力下被招募到停滞的复制叉,参与激活ATR-Chk1信号通路。功能缺失突变导致人类原始侏儒症,提示其在基因组稳定性中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*TRAIP regulates replication fork recovery and progression in a USP7-dependent manner*
**作者**:Hoffmann, S. et al.
**摘要**:通过TRAIP抗体染色和敲除模型,发现TRAIP通过去泛素化酶USP7调控复制叉重启。研究表明TRAIP缺失导致复制叉停滞和染色体断裂,揭示了其在复制压力应答中的分子机制。
---
3. **文献名称**:*TRAIP is a master regulator of DNA interstrand crosslink repair*
**作者**:Wu, R.A. et al.
**摘要**:使用TRAIP抗体进行免疫共沉淀和功能分析,证明TRAIP在DNA链间交联(ICL)修复中协调Fanconi贫血通路和核酸酶活性,其缺失导致细胞对交联剂高度敏感,强调其在DNA损伤修复中的核心地位。
---
这些文献均通过TRAIP抗体验证蛋白表达及定位,并阐明其在基因组稳定性、疾病及抗癌治疗中的潜在意义。如需具体DOI或年份,可进一步补充检索。
**Background of TRAIP Antibody**
The TRAF-interacting protein (TRAIP), also known as RNF206. is a ubiquitously expressed E3 ubiquitin ligase involved in critical cellular processes, including DNA damage response, cell cycle regulation, and genome stability maintenance. TRAIP interacts with components of the CRL4 ubiquitin ligase complex and plays a key role in resolving replication stress by promoting the repair of stalled replication forks. It is also essential for sister chromatid separation during mitosis. Dysregulation of TRAIP has been linked to various cancers, such as breast, ovarian, and liver cancers, due to its role in mitigating DNA replication errors and preventing genomic instability.
Mutations in the *TRAIP* gene are associated with congenital disorders like 3M syndrome, characterized by growth retardation and craniofacial abnormalities, underscoring its importance in developmental biology. TRAIP antibodies are vital research tools for studying its expression, subcellular localization, and interactions. They are used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence to explore TRAIP's molecular mechanisms in DNA repair pathways, tumorigenesis, and developmental defects. These antibodies help elucidate TRAIP's dual roles in health and disease, offering potential insights for therapeutic strategies targeting TRAIP-related pathologies.
×