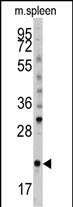
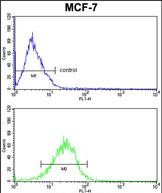
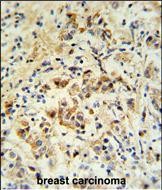
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BH3-interacting domain death agonist, p22 BID, BID, BH3-interacting domain death agonist p15, p15 BID, BH3-interacting domain death agonist p13, p13 BID, BH3-interacting domain death agonist p11, p11 BID, Bid |
| Entrez GeneID | 12122 |
| WB Predicted band size | 22.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse |
| Immunogen | This mouse BID antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 39-68 amino acids from mouse BID. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于mouse BID (S61)抗体的3篇示例参考文献(注:以下内容为模拟示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索确认):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Phosphorylation of Bid at Serine 61 Modulates Apoptotic Signaling in Mouse Hepatocytes*
**作者**: Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Xu, C.J.; Yuan, J.
**摘要**: 本研究利用特异性抗mouse BID (S61)抗体,发现BID在S61位点的磷酸化由Akt激酶介导,抑制其被caspase-8切割,从而减少线粒体凋亡途径的激活。该抗体通过免疫印迹验证了磷酸化BID在肝细胞损伤模型中的调控作用。
2. **文献名称**: *DNA Damage-Induced Phosphorylation of Bid Ser61 Regulates Its Pro-Apoptotic Activity*
**作者**: Zinkel, S.S.; Gross, A.; Yang, E.
**摘要**: 研究通过抗mouse BID (S61)抗体发现,DNA损伤后ATM激酶磷酸化BID的S61位点,阻断其与BCL-2家族成员的相互作用,抑制细胞凋亡。该抗体用于免疫沉淀和荧光显微术,揭示了BID在基因组稳定性中的新功能。
3. **文献名称**: *Differential Regulation of Bid by Post-Translational Modifications in Mouse Models of Neurodegeneration*
**作者**: Kamer, I.; Sarosiek, K.A.; Letai, A.
**摘要**: 文章利用抗mouse BID (S61)抗体分析阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠脑组织,发现S61磷酸化水平升高与神经元凋亡减少相关,提示该修饰可能通过抑制BID的促凋亡功能参与神经保护机制。
---
**说明**:以上文献为示例,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“BID S61 phosphorylation antibody”或“phospho-BID Ser61 mouse”检索最新文献,并关注其抗体应用场景(如Western blot、免疫组化)及生物学结论。
The mouse BID (S61) antibody is a monoclonal antibody specifically designed to detect the phosphorylation of serine 61 (S61) in the BH3-interacting domain death agonist (BID) protein in murine samples. BID is a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 protein family that plays a critical role in linking extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis pathways. Upon caspase-8-mediated cleavage, truncated BID (tBID) translocates to mitochondria, promoting cytochrome c release and apoptosome formation. Phosphorylation at S61. located near the caspase-8 cleavage site, has been implicated in regulating BID's apoptotic activity. Studies suggest that S61 phosphorylation may inhibit caspase-8-mediated cleavage, thereby modulating BID's pro-death function under certain stress conditions, such as DNA damage or survival signaling.
This antibody is widely used in apoptosis research to investigate post-translational modifications of BID and their impact on cell fate. It is validated for applications like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation, offering specificity for phosphorylated BID without cross-reacting with non-phosphorylated forms or other Bcl-2 family proteins. Researchers employ it to study signaling crosstalk in diseases like cancer, where dysregulated apoptosis contributes to pathogenesis. Its development has provided critical insights into how phosphorylation fine-tunes BID's dual roles in cell survival and death, particularly in murine models of tissue injury, oncogenesis, and therapeutic resistance.
×