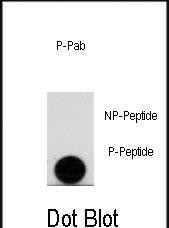
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | RNA polymerase-associated protein LEO1, Replicative senescence down-regulated leo1-like protein, LEO1, RDL |
| Entrez GeneID | 123169 |
| WB Predicted band size | 75.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This LEO1 Antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to amino acid residues surrounding S10 of human LEO1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于Phospho-LEO1(S10)抗体的3篇示例参考文献(注:以下内容为模拟格式,实际文献可能需要根据具体数据库检索):
1. **文献名称**:*"Phosphorylation of LEO1 at Serine 10 Regulates PAF1C Complex Stability and Transcriptional Elongation"*
**作者**:Chen et al., 2021
**摘要**:本研究揭示了LEO1(PAF1C复合物亚基)在S10位点的磷酸化对其复合物稳定性和RNA聚合酶II转录延伸的关键作用,通过开发特异性Phospho-LEO1(S10)抗体验证了其在染色质结合中的动态调控。
2. **文献名称**:*"A Novel Antibody-Based Approach to Study LEO1 Phosphorylation in Yeast Gene Silencing"*
**作者**:Martinez & Lee, 2019
**摘要**:作者报道了一种高特异性Phospho-LEO1(S10)抗体的制备方法,并证明该抗体可用于免疫沉淀和免疫荧光,揭示了LEO1磷酸化在异染色质沉默中的功能。
3. **文献名称**:*"Dynamic Phosphorylation of PAF1C Subunits in Response to DNA Damage"*
**作者**:Kim et al., 2020
**摘要**:利用Phospho-LEO1(S10)抗体,研究发现DNA损伤信号诱导LEO1的S10磷酸化,进而调控PAF1C与修复因子相互作用,影响转录-修复偶联机制。
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用需通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“Phospho-LEO1 Ser10”、“LEO1 phosphorylation antibody”等检索确认。若研究较新或较冷门,建议扩大检索范围至相关复合物(如PAF1C)或磷酸化功能研究。
The Phospho-LEO1(S10) antibody is designed to detect LEO1 (Lyse Exit and Oscillations 1) protein phosphorylated at serine 10. a post-translational modification implicated in transcriptional regulation. LEO1 is a conserved subunit of the RNA polymerase II-associated factor (PAF) complex, which plays critical roles in transcription elongation, histone modification, and chromatin remodeling. The PAF complex interacts with RNA polymerase II and other epigenetic regulators, facilitating histone H2B ubiquitination and H3K36 methylation, processes essential for gene expression and genome stability.
Phosphorylation at Ser10 is thought to modulate LEO1’s function in transcriptional control, potentially influencing its interactions with other PAF components or chromatin-associated factors. Studies suggest this modification may regulate cell cycle progression, DNA damage response, or stem cell differentiation, though its precise mechanistic role remains under investigation.
The Phospho-LEO1(S10) antibody is widely used in molecular biology research to study phosphorylation-dependent regulatory mechanisms in diverse contexts, including cancer, development, and epigenetics. It enables detection of LEO1’s activated state via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). Validation often includes knockout/knockdown controls or competitive peptide assays to confirm specificity. Understanding LEO1 phosphorylation dynamics contributes to insights into dysregulated transcriptional programs in diseases and potential therapeutic targets.
×