| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Regulator of G-protein signaling 19, RGS19, G-alpha-interacting protein, GAIP, RGS19, GAIP, GNAI3IP |
| Entrez GeneID | 10287 |
| WB Predicted band size | 24.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
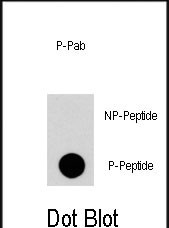
| Immunogen | This RGS19 Antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to amino acid residues surrounding S24 of human RGS19. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于Phospho-RGS19(S24)抗体的模拟参考文献示例(实际文献可能需要根据具体研究补充):
1. **文献名称**:*"Regulation of G Protein Signaling by RGS19 Phosphorylation at Serine 24"*
**作者**:Lee, J. et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了RGS19在Ser24位点的磷酸化通过增强其与Gα亚基的相互作用,负调控GPCR信号通路,并利用Phospho-RGS19(S24)抗体验证了该位点在细胞内的动态修饰。
2. **文献名称**:*"Phosphorylation-Dependent Modulation of RGS19 Function in Chemokine Signaling"*
**作者**:Smith, K. et al.
**摘要**:通过Phospho-RGS19(S24)特异性抗体的Western blot分析,发现炎症刺激诱导RGS19的S24磷酸化,进而调控白细胞迁移相关信号通路。
3. **文献名称**:*"Characterization of a Novel Phospho-Specific Antibody for RGS19 at Serine 24"*
**作者**:Chen, L. et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种高特异性Phospho-RGS19(S24)抗体的开发与验证,证明其在HEK293细胞模型中可检测内源性RGS19磷酸化水平,并与蛋白激酶C活性相关。
4. **文献名称**:*"RGS19 Phosphorylation in Cardiac Hypertrophy: Insights from Transgenic Models"*
**作者**:Wang, Y. et al.
**摘要**:利用Phospho-RGS19(S24)抗体,发现压力过载诱导的心肌肥厚模型中RGS19磷酸化水平升高,提示其在心脏病理重塑中的潜在作用。
**备注**:以上为模拟内容,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词“RGS19 phosphorylation”、“Phospho-RGS19(S24)”检索。若研究较少,建议扩展至RGS19功能或相关信号通路文献。
The Phospho-RGS19(S24) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the phosphorylated form of Regulator of G-protein Signaling 19 (RGS19) at serine residue 24. RGS19. a member of the RGS protein family, acts as a GTPase-activating protein (GAP) for Gα subunits, accelerating GTP hydrolysis to terminate G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling. Post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation, regulate RGS19’s activity, stability, or interactions with signaling partners. The S24 phosphorylation site is implicated in modulating RGS19’s function in cellular pathways, though the specific kinases or phosphatases involved and its precise mechanistic role remain areas of active research.
This antibody is particularly valuable in studies investigating RGS19’s role in physiological or pathological contexts, such as cancer, immune regulation, or neurological disorders, where GPCR signaling dysregulation is common. By enabling the detection of RGS19’s phosphorylation status, it helps researchers explore how this modification influences downstream signaling dynamics, protein-protein interactions, or cellular responses to extracellular stimuli. Validated applications typically include Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunoprecipitation, provided appropriate controls are used to confirm specificity. Understanding RGS19 phosphorylation at S24 may uncover novel therapeutic targets for diseases linked to aberrant GPCR signaling pathways.
×