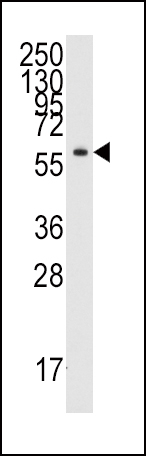
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Tyrosine--tRNA ligase, cytoplasmic, Tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase, TyrRS, Tyrosine--tRNA ligase, cytoplasmic, N-terminally processed, YARS |
| Entrez GeneID | 8565 |
| WB Predicted band size | 59.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This Tyrosyl tRNA synthetase (YARS) antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 450-479 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human Tyrosyl tRNA synthetase (YARS). |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于Tyrosyl tRNA synthetase (YARS)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Autoantibodies to tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies*
**作者**: Hirakata M, Suwa A, Takeda Y, et al.
**摘要内容**: 该研究报道了在特发性炎症性肌病(如多发性肌炎和皮肌炎)患者中检测到抗YARS抗体的存在。研究发现,这些抗体与间质性肺病(ILD)和关节炎显著相关,提示抗YARS抗体可能是抗合成酶综合征(ASS)的生物标志物之一。
2. **文献名称**: *Clinical manifestations and outcomes of anti-YARS antibody-positive patients in a large myositis cohort*
**作者**: Stone KB, Fertig N, Oddis CV, et al.
**摘要内容**: 研究通过分析大型肌炎患者队列,发现抗YARS抗体阳性患者常表现为ILD、发热和雷诺现象。与其他抗合成酶抗体(如抗Jo-1)相比,抗YARS抗体患者的肌肉症状较轻,但肺部并发症更为突出。
3. **文献名称**: *Anti-YARS autoantibodies in interstitial lung disease: A novel biomarker linking tRNA synthetase immunity to pulmonary pathology*
**作者**: Labirua-Butinet A, Bini V, Meneghetti S, et al.
**摘要内容**: 该研究探讨了抗YARS抗体在间质性肺病患者中的意义,发现其与快速进展的肺纤维化和治疗反应差相关。研究还提出YARS蛋白可能在肺部组织中异常表达,触发自身免疫反应。
---
以上文献均聚焦于抗YARS抗体在自身免疫性疾病(如抗合成酶综合征、ILD和肌炎)中的临床关联及机制研究。
Tyrosyl tRNA synthetase (YARS) is an enzyme responsible for charging tRNA with tyrosine during protein synthesis. Autoantibodies targeting YARS, classified as anti-aminoacyl tRNA synthetase antibodies, are primarily associated with autoimmune disorders, particularly **anti-synthetase syndrome (ASS)**, a subset of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM). These antibodies are part of a broader group, including anti-Jo-1 (the most common), that recognize aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Anti-YARS antibodies are less frequent but clinically significant, often linked to **interstitial lung disease (ILD)**, myositis, arthritis, and skin manifestations like mechanic’s hands.
The presence of anti-YARS antibodies aids in diagnosing ASS, though their rarity necessitates specialized testing (e.g., immunoprecipitation, line immunoassay). Patients with anti-YARS may exhibit variable disease severity, with ILD being a prominent feature influencing prognosis. Unlike anti-Jo-1. anti-YARS is associated with milder muscle involvement but a higher risk of progressive lung fibrosis.
Research suggests molecular mimicry or aberrant enzyme exposure during cell stress may trigger autoimmunity. Studies also explore YARS' non-canonical roles in angiogenesis or inflammation, potentially linking its autoantibodies to unique pathogenic pathways. Clinically, detection of anti-YARS guides tailored immunosuppressive therapy and ILD monitoring, emphasizing their role in personalized management of ASS. Further studies aim to clarify epitope specificity and prognostic implications.
×